Why Hasbro's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
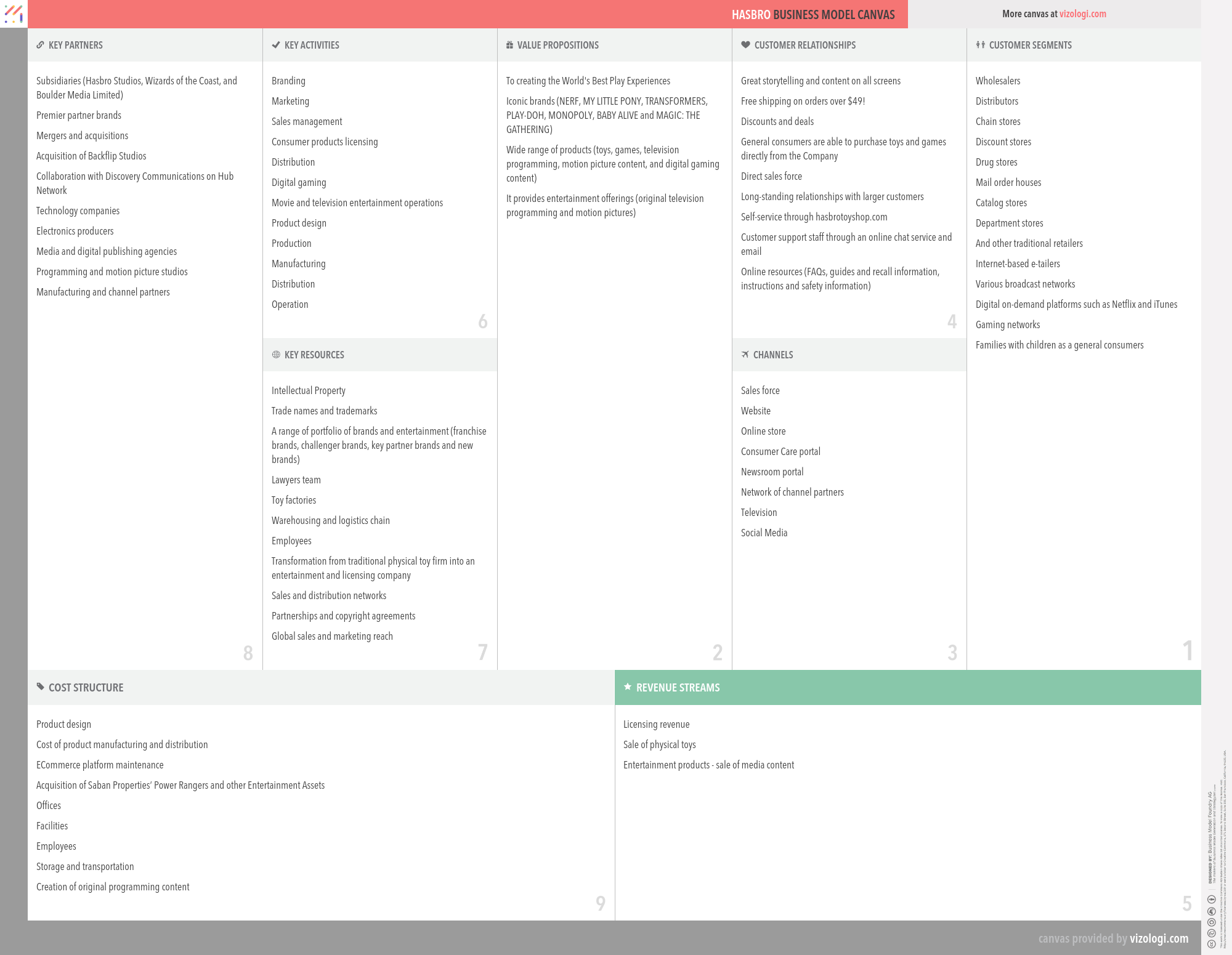
Hasbro’s Company Overview
Hasbro, Inc., together with its subsidiaries, operates as a play and entertainment company. The company’s U.S. and Canada segment markets and sells action figures, arts and crafts, and creative play products; electronic toys and related electronic interactive products; fashion and other dolls, infant products, play sets, preschool toys, plush products, and sports action blasters and accessories; and vehicles and toy-related specialty products, as well as traditional board games, and trading card and role-playing games primarily in the United States and Canada. Its International segment markets and sells toy and game products primarily in the European, the Asia Pacific, and Latin and South American regions.
https://www.hasbro.com/en-us/Country: Rhode Island
Foundations date: 1923
Type: Public
Sector: Consumer Goods
Categories: Retail
Hasbro’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing:
Emotional: fun/entertainment, badge value, provides access
Functional: quality, variety, sensory appeal, saves time, organizes
Hasbro’s Related Competitors
Hasbro’s Business Operations
Archetypes of business model design:
The business model archetypes include many business personalities and more than one business model linked to various goods or services. There is a common foundation behind the scenes of each unit, but from a management standpoint, each group may operate independently.
Brands consortium:
A collection of brands that coexist under the auspices of a parent business. The businesses in this pattern develop, produce, and market equipment. Their strength is in copywriting. Occasionally used to refer to a short-term agreement in which many companies (from the same or other industrial sectors or countries) combine their financial and personnel resources to execute a significant project benefiting all group members.
Cross-subsidiary:
When products and goods and products and services are integrated, they form a subsidiary side and a money side, maximizing the overall revenue impact. A subsidiary is a firm owned entirely or in part by another business, referred to as the parent company or holding company. A parent company with subsidiaries is a kind of conglomerate, a corporation that consists of several distinct companies; sometimes, the national or worldwide dispersion of the offices necessitates the establishment of subsidiaries.
Demarketing:
Excluding current clients that are unprofitable or who do not adhere to company principles. Efforts directed towards reducing (not eliminating) demand for a product that (1) a company cannot provide in sufficient quantities or (2) a firm does not want to sell in a particular area due to prohibitively expensive distribution or marketing expenses. Increased pricing, less promotion, and product redesign are all common demarketing tactics.
Direct selling:
Direct selling refers to a situation in which a company's goods are immediately accessible from the manufacturer or service provider rather than via intermediate channels. The business avoids the retail margin and any extra expenses connected with the intermediaries in this manner. These savings may be passed on to the client, establishing a consistent sales experience. Furthermore, such intimate touch may help to strengthen client connections. Finally, direct selling benefits consumers by providing convenience and service, such as personal demonstrations and explanations of goods, home delivery, and substantial satisfaction guarantees.
Discount club:
The discount club concept is built on perpetual high-discount deals utilized as a continual marketing plan or a brief period (usually one day). This might be seen as a reduction in the face value of an invoice prepared in advance of its payments in the medium or long term.
eCommerce:
Electronic commerce, or e-commerce (alternatively spelled eCommerce), is a business model, or a subset of a larger business model, that allows a company or person to do business via an electronic network, usually the internet. As a result, customers gain from increased accessibility and convenience, while the business benefits from integrating sales and distribution with other internal operations. Electronic commerce is prevalent throughout all four main market segments: business to business, business to consumer, consumer to consumer, and consumer to business. Ecommerce may be used to sell almost any goods or service, from books and music to financial services and airline tickets.
Franchising:
A franchise is a license that a business (franchisee) obtains to get access to a business's secret knowledge, procedures, and trademarks to promote a product or provide services under the company's business name. The franchisee typically pays the franchisee an initial startup cost and yearly licensing fees in return for obtaining the franchise.
From push to pull:
In business, a push-pull system refers to the flow of a product or information between two parties. Customers pull the products or information they need on markets, while offerers or suppliers push them toward them. In logistics and supply chains, stages often operate in both push and pull modes. For example, push production is forecasted demand, while pull production is actual or consumer demand. The push-pull border or decoupling point is the contact between these phases. Wal-Mart is a case of a company that employs a push vs. a pull approach.
Ingredient branding:
Ingredient branding is a kind of marketing in which a component or ingredient of a product or service is elevated to prominence and given its own identity. It is the process of developing a brand for an element or component of a product in order to communicate the ingredient's superior quality or performance. For example, everybody is aware of the now-famous Intel Inside and its subsequent success.
Layer player:
Companies that add value across many markets and sectors are referred to be layer players. Occasionally, specialist companies achieve dominance in a specific niche market. The effectiveness of their operations, along with their economies of size and footprint, establish the business as a market leader.
Licensing:
A formal agreement in which the owner of the copyright, know-how, patent, service mark, trademark, or other intellectual property grants a licensee the right to use, manufacture, and sell copies of the original. These agreements often restrict the licensee's scope or area of operation, define whether the license is exclusive or non-exclusive, and stipulate whether the licensee will pay royalties or another kind of compensation in return. While licensing agreements are often used to commercialize the technology, franchisees also utilize them to encourage the sale of products and services.
Make and distribute:
In this arrangement, the producer creates the product and distributes it to distributors, who oversee the goods' ongoing management in the market.
Recommended companies based on your search: