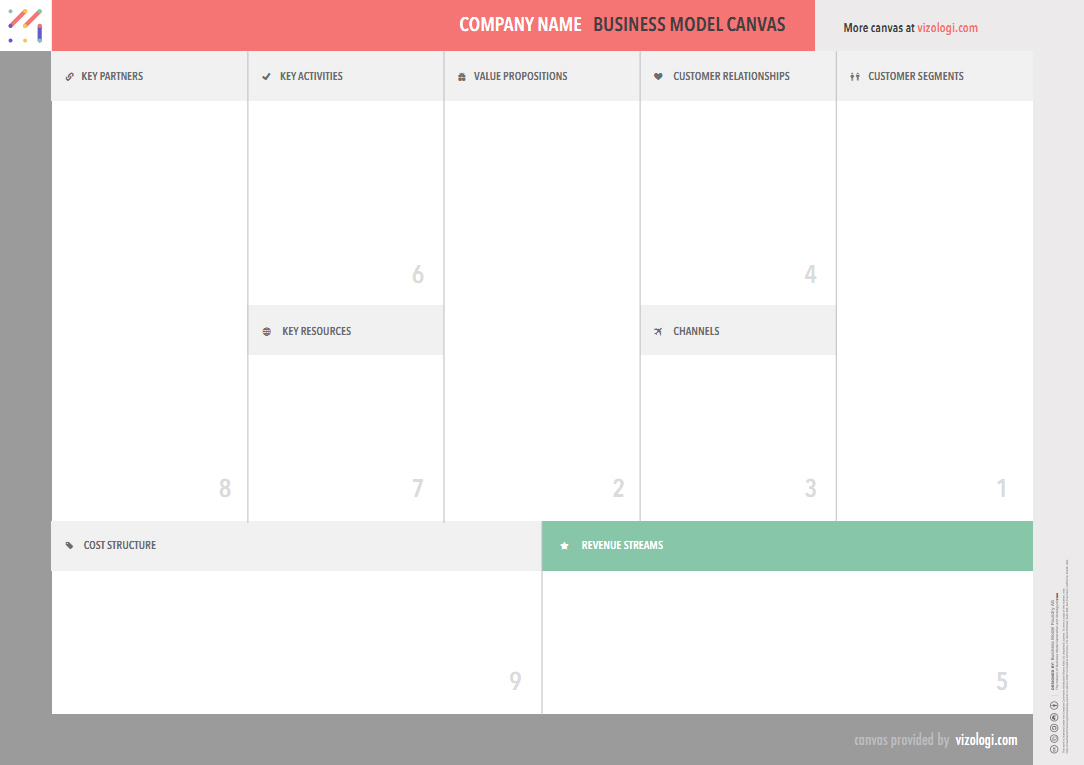
What is the Business Model Canvas?
Introduction To Business Model Methodology:
On the one hand, the business model is about finding new ways to add value to a business in the face of rapidly changing circumstances – economically, socially, environmentally, technologically, politically, globally, nationally, and locally.
A business model is also the company’s plan to generate revenue and make a profit from operations.
On the other hand, the business model canvas is a tool invented by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, used to analyze, describe and design your business models. This tool is used by several million business creators globally.
By simply aligning your business activities creatively and simply, business model canvas (which is a graphic representation of several variables) helps you stay in touch with your business’s vital parts.
When you utilize the nine key business elements provided by the canvas, you will remain aware of your project’s big picture. The Business model canvas template can be considered the famous spread document of Business Modeling history.
Business Model Canvas Explained.
Let us go through each of the building blocks of a business model canvas more thoroughly; each step number sets a recommendation about the logical thinking to follow to complete your business model canvas in a question of minutes:
The building blocks that make up a business model canvas as created by Osterwalder and Yves are classified into nine categories.
1/Customer segments:
- Who are your customers?
- What do they feel, think, see or do?
- Who is your most important customer?
Since most organizations meet several consumer groups’ needs, it is only ideal for separating them into what is known as customer segments.
The most critical piece of the strategy puzzle is identifying exactly who the public you are focusing on, the industry, the final user, your client, and the whole ecosystem where your proposal is pointing.
Then, identifying each group’s requirements and specific needs and the value attached to each one will be easier, which will enable better targeting of services and products to meet these requirements and needs.
As a result, customers enjoy greater satisfaction and experience, which will consecutively play a part in the value proposition.
2/Value proposition:
- What is the value proposition in the business model canvas?
- What are the core values that you deliver to your customers?
- What is convincing or persuasive about the proposal?
- What needs of clients are you presently satisfying or meeting?
- Why do your customers buy and use your products?
This is the most important reason why an organization exists in the first instance. The value proposition is all about meeting the needs of customers.
How then can a company set itself apart from its competitors?
This is possible by focusing on attributes like quantity such as the service, price, speed, and conditions attached to delivery and concentrate on quality such as brand status, design, customer satisfaction, and experience.
3/Distribution channels:
- What are the channels via which your customers want to be reached?
- Which of these channels are the best and most effective in reaching your target audience?
- How are these channels promoted, sold as well as delivered to target customers?
- Why are you even using these channels in the first instance?
- How much do they cost?
- How can you aggregate these channels into your routine as well as that of your customers as well?
An establishment deals with several channels, which include sales, distribution, and communications. This is not about the contacts of customers or how a company communicates with its clients.
Decisive elements contribute to creating distribution channels depending on the purchase and delivery of the service or product.
There are five different stages when it comes to customers. They are:
- Product awareness
- Purchase
- Delivery
- Evaluation and satisfaction
- Aftersales
Combining online (eCommerce) with off-line (brick-and-mortar shops) channels is advisable if your organization’s goal is to maximize the distribution channels to reach as many clients as possible.
4/Customer relationships:
- How do you be in touch with the target customer throughout their journey?
- Is there any relationship that your target audiences expect you to establish?
- Is it possible to integrate that into your business regarding format and cost?
- How can you do this?
It is essential to interact with customers. When your customer base broadens, you must divide your target audience into different groups. Each group of clients has needs that are peculiar to them.
When you anticipate your customers’ needs, the company will be able to invest in different customers. Thanks to web personalization, it is now possible to offer specific products or services to every customer.
A good product or service engenders steady customer relationships that will be guaranteed in the nearest future.
The left side of the canvas is composed of four blocks.
5/Revenue streams:
- What are revenue streams in the business model canvas?
- How does the business make money from its value proposition?
- What are the values their clients are willing to pay?
- How and what do they pay recently?
- What is your preferred mode of payment?
- How much does every stream of revenue contribution to the total income?
Besides the cost structure, revenue streams will require a clear insight into its model of income.
How many customers does any business enterprise need annually to make a profit?
The revenue stream is a driver of cost; other than the revenue generated from the sales of products or goods, licensing, subscription fees, sponsoring, lease income, and advertising can also be another option.
6/Key activities:
- What are the strategic things the business delivers when it comes to its propositions?
- What are the most necessary activities to implement or focus on: revenue streams, customer relationships, distribution channels, etc.?
An organization should not focus only on production but should pay heed to the approach to solve a problem, networking, and the service or product’s value.
Thorough understanding of the value proposition, i.e., the statement of business strategy, can only be achieved when entrepreneurs have a sound knowledge of an organization’s fundamental activities.
By knowing what value you are going to add to a customer’s life, the company will be able to foster an excellent relationship with existing clients.
This will also be useful when the organization carefully inspects new customers and draws them close while keeping competitors at a safe distance.
7/Key resources:
- What are the key resources that your value proposition needs?
- What are the strategic assets that are unique to your business and will give it a competitive edge?
- What are the most valuable resources: customer relationships, distribution channels, revenue streams, etc.?
Resources can be categorized as financial, physical, intellectual, or human resources. Every organization needs resources to perform effectively.
Financial resources involve the flow of funds and income sources, while physical resources include assets like business equipment, etc. Intellectual resources could be knowledge, patents, and brands, while human resources cover staff.
8/Key partners:
- Who are your major partners/suppliers?
- What do you use as motivation for partnerships?
- What is your organization incapable of doing so you can pay more attention to its key activities?
It is vital for organizations, whether startups or existing, to form strategic alliances with partners. This makes it easier to fight the competition more evenly and is ideal for combining specialization and knowledge.
Knowing in advance which partners may prove to be valuable to your business will collect essential data or information from reinforcing your decision to choose them as partners.
Last but not least, the third module according to the practical and safe side of the logic.
9/Cost structure:
- What is the cost structure in the business model canvas?
- What costs the most in your business?
- How are the fees linked to the revenue?
- Which of these key activities/resources are most costly?
Using the business model canvas can help you gain much insight into cost structure, thus informing the organization about the minimum turnover that will be required to make a profit. The cost structure takes variable and constant costs as well as economies of scale and benefit advantages into consideration.
When it becomes apparent that the organization is not generating as much revenue as desired, whereby more investments are required, they must make adjustments to the costs.
At times like this, a majority of organizations usually prefer scraping several key resources.
Tips and recommendations.
- When developing your product value proposition, the entrepreneur must first ask himself what kind of problem they solve with the product or service they offer.
- The whole customer cake is broken down into segments according to how an organization’s products or services meet a particular segment requirement.
- However, don’t fall in love with your first idea and instead design alternative business models for the same effect, service or technology.
- Try to understand that your business model canvas is a live document!
- The Canvas Business Model is a unique tool to help entrepreneurs build a global vision of their business. Just in case the recommendation comes to make a business plan once the idea has been validated with your canvas.
- However, organizations that compete for prices, or in some cases, even offering free services, often have different business models to support the team.