Why JBS's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
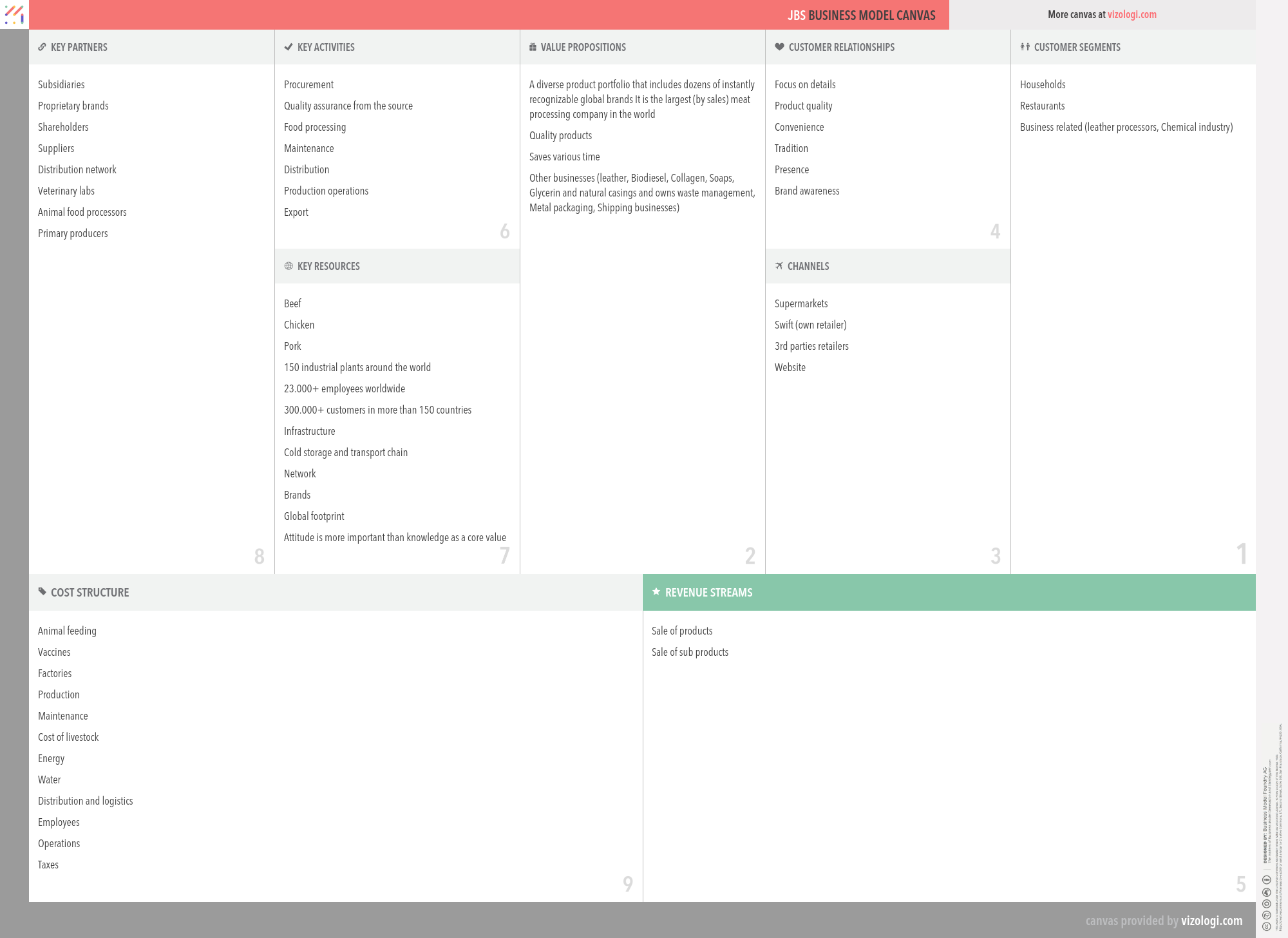
JBS’s Company Overview
Jbs SA, formerly Friboi Ltda, is a Brazil-based company primarily engaged in the meat processing sector. The company's activities are divided into three business Segments: Beef, which operates slaughter, cold storage and meat processing facilities for the production of beef preservatives, fat, feed and derivate products; Chicken, which includes refrigerated poultry meat and meat cuts supplied to restaurant chains, food processors, distributors and supermarkets, among others, and Pork, which includes slaughters, processing, cold storage of pork meat products and by-products. Its products are distributed under various brand names, such as Friboi, Swift, and Bertin. In addition, the company is involved in the leather tanning, aluminum cans production, industrial waste management, soap, glycerin and biodiesel production, as well as transportation, among others. The company operates in the United States, Canada, Mexico, Argentina, and Paraguay, among others.
http://jbs.com.brCountry: Brazil
Foundations date: 1953
Type: Public
Sector: Industrials
Categories: Food & Beverages
JBS’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing:
Emotional: wellness, design/aesthetics
Functional: reduces effort, quality, variety, sensory appeal, integrates, organizes
JBS’s Related Competitors
JBS’s Business Operations
Brands consortium:
A collection of brands that coexist under the auspices of a parent business. The businesses in this pattern develop, produce, and market equipment. Their strength is in copywriting. Occasionally used to refer to a short-term agreement in which many companies (from the same or other industrial sectors or countries) combine their financial and personnel resources to execute a significant project benefiting all group members.
Bundling:
Multiple products or services have been bundled together to enhance the value. Bundling is a marketing technique in which goods or services are bundled to be sold as a single entity. Bundling enables the purchasing of several goods and services from a single vendor. While the goods and services are often linked, they may also consist of different items that appeal to a particular market segment.
Cross-selling:
Cross-selling is a business strategy in which additional services or goods are offered to the primary offering to attract new consumers and retain existing ones. Numerous businesses are increasingly diversifying their product lines with items that have little resemblance to their primary offerings. Walmart is one such example; they used to offer everything but food. They want their stores to function as one-stop shops. Thus, companies mitigate their reliance on particular items and increase overall sustainability by providing other goods and services.
Cross-subsidiary:
When products and goods and products and services are integrated, they form a subsidiary side and a money side, maximizing the overall revenue impact. A subsidiary is a firm owned entirely or in part by another business, referred to as the parent company or holding company. A parent company with subsidiaries is a kind of conglomerate, a corporation that consists of several distinct companies; sometimes, the national or worldwide dispersion of the offices necessitates the establishment of subsidiaries.
Customer loyalty:
Customer loyalty is a very successful business strategy. It entails giving consumers value that extends beyond the product or service itself. It is often provided through incentive-based programs such as member discounts, coupons, birthday discounts, and points. Today, most businesses have some kind of incentive-based programs, such as American Airlines, which rewards customers with points for each trip they take with them.
Hypermarket:
Disrupts by 'brand bombing' competitors, often by offering below cost. Hypermarkets, like other large-scale retailers, generally operate on a high-volume, low-margin basis. They typically span a space of 5,000 to 15,000 square meters (54,000 to 161,000 square feet) and stock more than 200,000 different brands of goods.
Ingredient branding:
Ingredient branding is a kind of marketing in which a component or ingredient of a product or service is elevated to prominence and given its own identity. It is the process of developing a brand for an element or component of a product in order to communicate the ingredient's superior quality or performance. For example, everybody is aware of the now-famous Intel Inside and its subsequent success.
Integrator:
A systems integrator is an individual or business specializing in integrating component subsystems into a unified whole and ensuring that those subsystems work correctly together. A process is known as system integration. Gains in efficiency, economies of scope, and less reliance on suppliers result in cost reductions and may improve the stability of value generation.
Long tail:
The long tail is a strategy that allows businesses to realize significant profit out of selling low volumes of hard-to-find items to many customers instead of only selling large volumes of a reduced number of popular items. The term was coined in 2004 by Chris Anderson, who argued that products in low demand or with low sales volume can collectively make up market share that rivals or exceeds the relatively few current bestsellers and blockbusters but only if the store or distribution channel is large enough.
Make and distribute:
In this arrangement, the producer creates the product and distributes it to distributors, who oversee the goods' ongoing management in the market.
Regular replacement:
It includes items that must be replaced on a regular basis; the user cannot reuse them. Consumables are products utilized by people and companies and must be returned regularly due to wear and tear or depletion. Additionally, they may be described as components of a final product consumed or irreversibly changed throughout the production process, including semiconductor wafers and basic chemicals.
Shop in shop:
A store-within-a-store, sometimes known as a shop-in-shop, is an arrangement in which a retailer leases out a portion of its retail space to another business to operate another independent store. This arrangement is prevalent with gas stations and supermarkets. In addition, numerous bookstores collaborate with coffee shops since consumers often want a spot to relax and enjoy a beverage while browsing. Frequently, the shop-within-a-store is owned by a manufacturer who operates an outlet inside a retailer's store.
Spectrum retail:
Utilizes a multi-tiered e-commerce approach. The firm first focused on business-to-consumer connections with its customers and business-to-business ties with its suppliers. Still, it later expanded to include customer-to-business transactions after recognizing the importance of customer evaluations in product descriptions. It now also enables customer-to-customer transactions by establishing a marketplace that serves as a middleman for such transactions. The company's platform enables nearly anybody to sell almost anything.
Supermarket:
A supermarket is a self-service store arranged into aisles and has many foods and home goods. It is bigger and has a greater variety than traditional grocery shops but is smaller and offers a more limited selection than a hypermarket or big-box market. Supermarkets are usually chain shops supplied by their parent firms' distribution centers, allowing for more significant economies of scale. In addition, supermarkets often provide items at competitive rates by using their purchasing power to negotiate lower pricing from producers than smaller shops can.
Supply chain:
A supply chain is a network of companies, people, activities, data, and resources that facilitate the movement of goods and services from supplier to consumer. The supply chain processes natural resources, raw materials, and components into a completed product supplied to the ultimate consumer. In addition, used goods may re-enter the distribution network at any point where residual value is recyclable in advanced supply chain systems. Thus, value chains are connected through supply chains.
Recommended companies based on your search: