Why Parse.ly's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
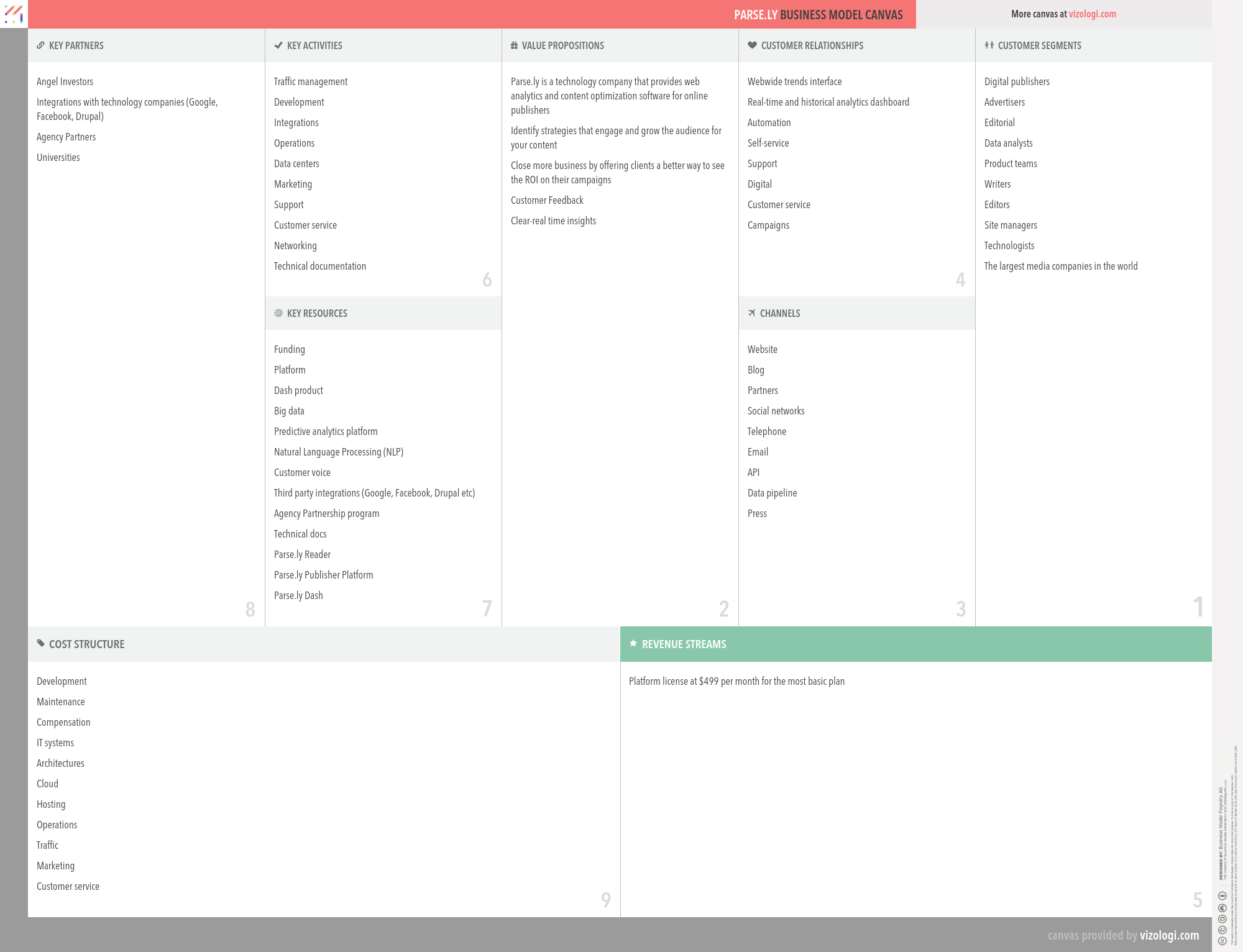
Parse.ly’s Company Overview
Parse.ly is the web's attention engine. Their products help the best sites on the web improve digital audience engagement. Parse.ly is a content optimization platform for online publishers. Parse.ly's product, Dash, is built on top of the Parse.ly platform. Dash parses articles on a publisher's site and then analyzes them to identify data around metrics that are specific for publishers such as topics, authors, sections, and referrers.
http://www.parsely.com/Parse.ly’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: self-actualization
Emotional: badge value, provides access, attractiveness, reduces anxiety, design/aesthetics
Functional: saves time, simplifies, integrates, connects, informs, quality, reduces effort, informs, organizes, avoids hassles, sensory appeal
Parse.ly’s Related Competitors
Parse.ly’s Business Operations
Codifying a distinctive service capability:
Since their inception, information technology systems have aided in automating corporate operations, increasing productivity, and maximizing efficiency. Now, businesses can take their perfected processes, standardize them, and sell them to other parties. In today's corporate environment, innovation is critical for survival.
Consumerization of work:
Consumerization of IT (consumerization) is a term that refers to the process by which Information Technology (IT) begins in the consumer market and then spreads to business and government organizations, primarily as a result of employees utilizing popular consumer market technologies and methods at home and afterward bringing them in the workplace.
Corporate innovation:
Innovation is the outcome of collaborative creativity in turning an idea into a feasible concept, accompanied by a collaborative effort to bring that concept to life as a product, service, or process improvement. The digital era has created an environment conducive to business model innovation since technology has transformed how businesses operate and provide services to consumers.
Data as a Service (DaaS):
Data as a Service (DaaS) is a relative of Software as a Service in computing (SaaS). As with other members of the as a service (aaS) family, DaaS is based on the idea that the product (in this instance, data) may be delivered to the user on-demand independent of the provider's geographic or organizational isolation from the customer. Additionally, with the advent[when?] of service-oriented architecture (SOA), the platform on which the data sits has become unimportant. This progression paved the way for the relatively recent new idea of DaaS to arise.
Digital:
A digital strategy is a strategic management and a business reaction or solution to a digital issue, which is often best handled as part of a broader company plan. A digital strategy is frequently defined by the application of new technologies to existing business activities and a focus on enabling new digital skills for their company (such as those formed by the Information Age and frequently as a result of advances in digital technologies such as computers, data, telecommunication services, and the World wide web, to name a few).
Digital transformation:
Digitalization is the systematic and accelerated transformation of company operations, processes, skills, and models to fully exploit the changes and possibilities brought about by digital technology and its effect on society. Digital transformation is a journey with many interconnected intermediate objectives, with the ultimate aim of continuous enhancement of processes, divisions, and the business ecosystem in a hyperconnected age. Therefore, establishing the appropriate bridges for the trip is critical to success.
Digitization:
This pattern is based on the capacity to convert current goods or services into digital versions, which have several benefits over intangible products, including increased accessibility and speed of distribution. In an ideal world, the digitalization of a product or service would occur without compromising the consumer value proposition. In other words, efficiency and multiplication achieved via digitalization do not detract from the consumer's perceived value. Being digitally sustainable encompasses all aspects of sustaining the institutional framework for developing and maintaining digital objects and resources and ensuring their long-term survival.
Licensing:
A formal agreement in which the owner of the copyright, know-how, patent, service mark, trademark, or other intellectual property grants a licensee the right to use, manufacture, and sell copies of the original. These agreements often restrict the licensee's scope or area of operation, define whether the license is exclusive or non-exclusive, and stipulate whether the licensee will pay royalties or another kind of compensation in return. While licensing agreements are often used to commercialize the technology, franchisees also utilize them to encourage the sale of products and services.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a class of cloud computing services that enable users to create, operate, and manage apps without the burden of establishing and maintaining the infrastructure usually involved with designing and developing an app.
Product innovation:
Product innovation is the process of developing and introducing a new or better version of an existing product or service. This is a broader definition of innovation than the generally recognized definition, which includes creating new goods that are considered innovative in this context. For example, Apple launched a succession of successful new products and services in 2001?the iPod, the iTunes online music service, and the iPhone?which catapulted the firm to the top of its industry.
Self-service:
A retail business model in which consumers self-serve the goods they want to buy. Self-service business concepts include self-service food buffets, self-service petrol stations, and self-service markets. Self-service is available through phone, online, and email to automate customer support interactions. Self-service Software and self-service applications (for example, online banking apps, shopping portals, and self-service check-in at airports) are becoming more prevalent.
Solution provider:
A solution provider consolidates all goods and services in a particular domain into a single point of contact. As a result, the client is supplied with a unique know-how to improve efficiency and performance. As a Solution Provider, a business may avoid revenue loss by broadening the scope of the service it offers, which adds value to the product. Additionally, close client interaction enables a better understanding of the customer's habits and requirements, enhancing goods and services.
Trading data:
Combining disparate data sets enables businesses to develop a variety of new offerings for complementary companies. Robustness is a property that describes a model's, test's, or system's ability to perform effectively when its variables or assumptions are changed, ensuring that a robust concept operates without fail under various conditions. In general, robustness refers to a system's capacity to deal with unpredictability while remaining practical.
Recommended companies based on your search: