Why Tchibo's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
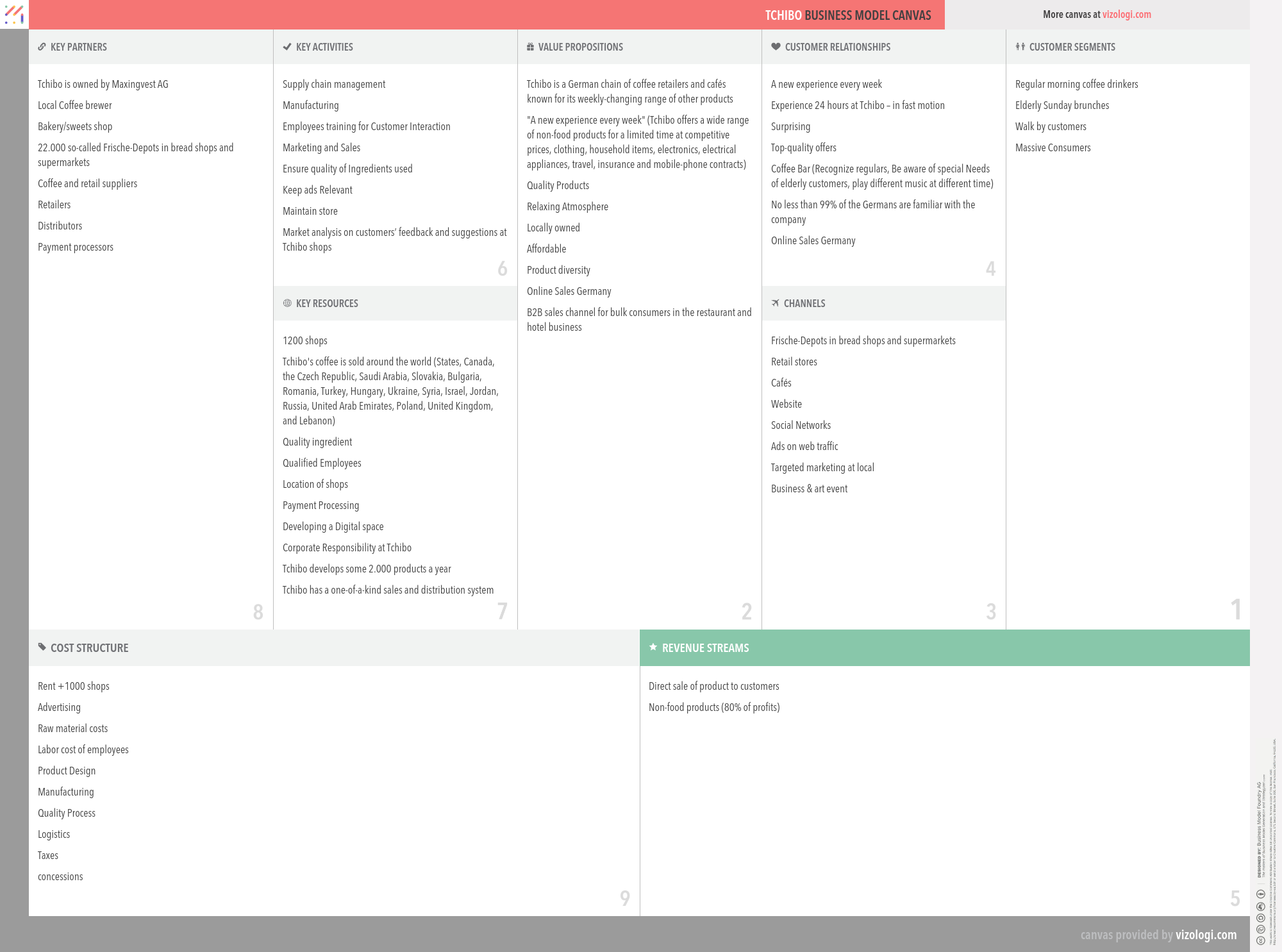
Tchibo’s Company Overview
Founded in 1949 by Max Herz, Tchibo has been synonymous with freshness and quality in the coffee market for over 65 years. Originally a coffee mail-order firm, it has evolved into an international company and operates in many more business sectors than the traditional selling of coffee. Over the years, Tchibo has systematically expanded its range and distribution paths, ensuring diversity and quality the world over with strong brands also known for its weekly-changing range of other products. Tchibo has expanded its product range and is now selling services such as travel, insurance and mobile-phone contracts. With over 1000 shops, Tchibo is one of Germany's largest retail chains. The company is headquartered in Hamburg.
https://www.tchibo.com/servlet/content/312682/-/starteseite-deutsch_en.htmlCountry: Germany
Foundations date: 1949
Type: Private
Sector: Consumer Goods
Categories: Retail
Tchibo’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: affiliation/belonging
Emotional: attractiveness, rewards me, reduces anxiety, badge value
Functional: integrates, quality, variety, sensory appeal
Tchibo’s Related Competitors
Tchibo’s Business Operations
Archetypes of business model design:
The business model archetypes include many business personalities and more than one business model linked to various goods or services. There is a common foundation behind the scenes of each unit, but from a management standpoint, each group may operate independently.
Best in class services:
When a firm brings a product to market, it must first create a compelling product and then field a workforce capable of manufacturing it at a competitive price. Neither task is simple to perform effectively; much managerial effort and scholarly study have been dedicated to these issues. Nevertheless, providing a service involves another aspect: managing clients, who are consumers of the service and may also contribute to its creation.
Bundling:
Multiple products or services have been bundled together to enhance the value. Bundling is a marketing technique in which goods or services are bundled to be sold as a single entity. Bundling enables the purchasing of several goods and services from a single vendor. While the goods and services are often linked, they may also consist of different items that appeal to a particular market segment.
Cross-selling:
Cross-selling is a business strategy in which additional services or goods are offered to the primary offering to attract new consumers and retain existing ones. Numerous businesses are increasingly diversifying their product lines with items that have little resemblance to their primary offerings. Walmart is one such example; they used to offer everything but food. They want their stores to function as one-stop shops. Thus, companies mitigate their reliance on particular items and increase overall sustainability by providing other goods and services.
Cross-subsidiary:
When products and goods and products and services are integrated, they form a subsidiary side and a money side, maximizing the overall revenue impact. A subsidiary is a firm owned entirely or in part by another business, referred to as the parent company or holding company. A parent company with subsidiaries is a kind of conglomerate, a corporation that consists of several distinct companies; sometimes, the national or worldwide dispersion of the offices necessitates the establishment of subsidiaries.
Decomposition:
Simplifying many product kinds inside a product group or set of goods. A technique for doing business analysis in which a complex business process is dissected to reveal its constituent parts. Functional decomposition is a technique that may be used to contribute to an understanding and management of large and complicated processes and assist in issue solving. Additionally, functional decomposition is utilized in computer engineering to aid in the creation of software.
Direct selling:
Direct selling refers to a situation in which a company's goods are immediately accessible from the manufacturer or service provider rather than via intermediate channels. The business avoids the retail margin and any extra expenses connected with the intermediaries in this manner. These savings may be passed on to the client, establishing a consistent sales experience. Furthermore, such intimate touch may help to strengthen client connections. Finally, direct selling benefits consumers by providing convenience and service, such as personal demonstrations and explanations of goods, home delivery, and substantial satisfaction guarantees.
eCommerce:
Electronic commerce, or e-commerce (alternatively spelled eCommerce), is a business model, or a subset of a larger business model, that allows a company or person to do business via an electronic network, usually the internet. As a result, customers gain from increased accessibility and convenience, while the business benefits from integrating sales and distribution with other internal operations. Electronic commerce is prevalent throughout all four main market segments: business to business, business to consumer, consumer to consumer, and consumer to business. Ecommerce may be used to sell almost any goods or service, from books and music to financial services and airline tickets.
Enterprise unbundled:
Unbundling is a business practice that recognizes that a company may have three primary focuses: client connections, product innovation, and infrastructure. Moreover, three of these elements may coexist in big businesses, creating a complex model that needs significant resources to operate effectively. Thus, unbundling is a crucial idea for any enterprise's future success. Additionally referred to as deconstruction or disaggregation, this benign word refers to a dominating force that propels digital change into the heart of whole sectors.
Experience selling:
An experience in the sales model describes how a typical user perceives or comprehends a system's operation. A product or service's value is enhanced when an extra customer experience is included. Visual representations of experience models are abstract diagrams or metaphors derived from recognizable objects, actions, or systems. User interfaces use a range of experience models to help users rapidly comprehend what is occurring in the design, where they are, and what they may do next. For example, a software experience model may depict the connection between two applications and the relationship between an application and different navigation methods and other system or software components.
Fast fashion:
Fast fashion is a phrase fashion retailers use to describe how designs travel rapidly from the catwalk to catch current fashion trends. The emphasis is on optimizing specific supply chain components to enable these trends to be developed and produced quickly and affordably, allowing the mainstream customer to purchase current apparel designs at a reduced price.
Make more of It:
The business invests time and money in developing in-house expertise and development that may be used both internally and outside to sell goods or services to clients or third parties. AWS was created to meet Amazon's cloud computing requirements. They quickly discovered that they could offer their services to end-users. At the moment, AWS accounts for about 11% of Amazon's overall income.
Regular replacement:
It includes items that must be replaced on a regular basis; the user cannot reuse them. Consumables are products utilized by people and companies and must be returned regularly due to wear and tear or depletion. Additionally, they may be described as components of a final product consumed or irreversibly changed throughout the production process, including semiconductor wafers and basic chemicals.
Reseller:
Resellers are businesses or individuals (merchants) that acquire products or services to resell them instead of consuming or utilizing them. This is often done for financial gain (but could be resold at a loss). Resellers are well-known for doing business on the internet through websites. One instance is the telecommunications sector, in which corporations purchase surplus transmission capacity or take the call from other providers and resell it to regional carriers.
Shop in shop:
A store-within-a-store, sometimes known as a shop-in-shop, is an arrangement in which a retailer leases out a portion of its retail space to another business to operate another independent store. This arrangement is prevalent with gas stations and supermarkets. In addition, numerous bookstores collaborate with coffee shops since consumers often want a spot to relax and enjoy a beverage while browsing. Frequently, the shop-within-a-store is owned by a manufacturer who operates an outlet inside a retailer's store.
Supermarket:
A supermarket is a self-service store arranged into aisles and has many foods and home goods. It is bigger and has a greater variety than traditional grocery shops but is smaller and offers a more limited selection than a hypermarket or big-box market. Supermarkets are usually chain shops supplied by their parent firms' distribution centers, allowing for more significant economies of scale. In addition, supermarkets often provide items at competitive rates by using their purchasing power to negotiate lower pricing from producers than smaller shops can.
Take the wheel:
Historically, the fundamental principles for generating and extracting economic value were rigorous. Businesses attempted to implement the same business concepts more effectively than their rivals. New sources of sustained competitive advantage are often only accessible via business model reinvention driven by disruptive innovation rather than incremental change or continuous improvement.
Recommended companies based on your search: