Why Cheese Board Collective's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
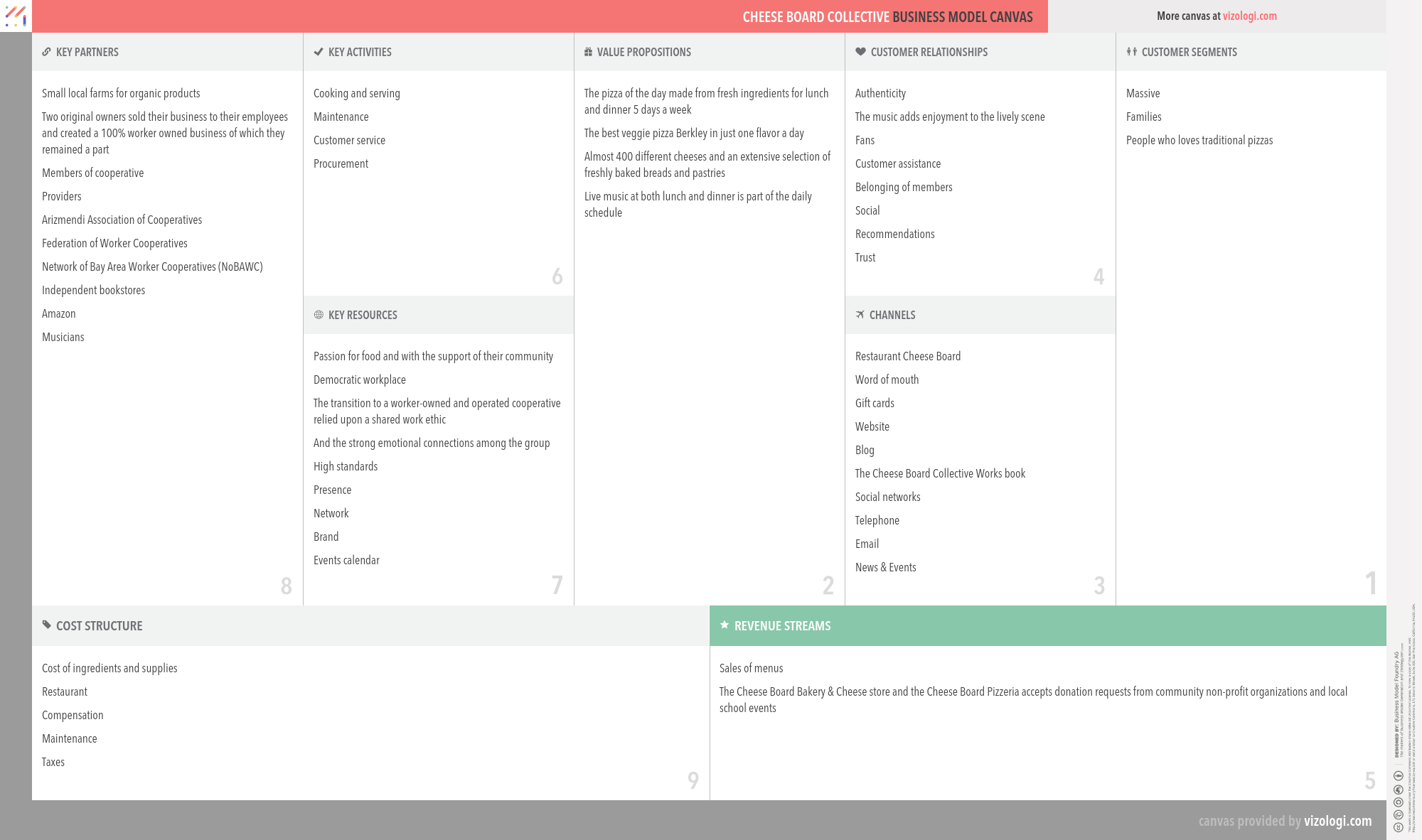
Cheese Board Collective’s Company Overview
The Cheese Board Collective in Berkeley, California, comprises two worker owned and operated businesses: a cheese shop/bakery commonly referred to as "The Cheese Board", and a pizzeria known as "Cheese Board Pizza". Along with Peet's Coffee, the Cheese Board is known for its role in starting the North Shattuck neighborhood of Berkeley on its way to becoming famous as a culinary destination: the "Gourmet Ghetto".
www.cheeseboardcollective.coopCountry: California
Foundations date: 1967
Type: Private
Sector: Consumer Services
Categories: Restaurants
Cheese Board Collective’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: affiliation/belonging
Emotional: attractiveness, rewards me, badge value, nostalgia
Functional: connects, quality, variety, sensory appeal
Cheese Board Collective’s Related Competitors
Cheese Board Collective’s Business Operations
Aikido:
The aikido business model is often characterized as using a competitor's strength to get an edge over them. This is accomplished through finding weaknesses in a competitor's strategic position. In addition, it adds to marketing sustainability by exposing rivals' flaws, finding internal and external areas for development, and attracting consumers via specific product offers that deviate from the norm.
Consumers' co-operative:
Consumers' co-operative are enterprises owned by consumers and managed democratically which aim at fulfilling the needs and aspirations of their members. They operate within the market system, independently of the state, as a form of mutual aid, oriented toward service rather than pecuniary profit. Consumers' cooperatives often take the form of retail outlets owned and operated by their consumers, such as food co-ops.
Culture is brand:
It requires workers to live brand values to solve issues, make internal choices, and provide a branded consumer. Developing a distinctive and enduring cultural brand is the advertising industry's holy grail. Utilizing the hazy combination of time, attitude, and emotion to identify and replicate an ideology is near to marketing magic.
Customer loyalty:
Customer loyalty is a very successful business strategy. It entails giving consumers value that extends beyond the product or service itself. It is often provided through incentive-based programs such as member discounts, coupons, birthday discounts, and points. Today, most businesses have some kind of incentive-based programs, such as American Airlines, which rewards customers with points for each trip they take with them.
Direct selling:
Direct selling refers to a situation in which a company's goods are immediately accessible from the manufacturer or service provider rather than via intermediate channels. The business avoids the retail margin and any extra expenses connected with the intermediaries in this manner. These savings may be passed on to the client, establishing a consistent sales experience. Furthermore, such intimate touch may help to strengthen client connections. Finally, direct selling benefits consumers by providing convenience and service, such as personal demonstrations and explanations of goods, home delivery, and substantial satisfaction guarantees.
Experience:
Disrupts by offering a better understanding that customers are willing to pay for. Experience companies that have progressed may begin charging for the value of the transformation that an experience provides. An experienced company charges for the feelings consumers get as a result of their interaction with it.
Experience selling:
An experience in the sales model describes how a typical user perceives or comprehends a system's operation. A product or service's value is enhanced when an extra customer experience is included. Visual representations of experience models are abstract diagrams or metaphors derived from recognizable objects, actions, or systems. User interfaces use a range of experience models to help users rapidly comprehend what is occurring in the design, where they are, and what they may do next. For example, a software experience model may depict the connection between two applications and the relationship between an application and different navigation methods and other system or software components.
Franchising:
A franchise is a license that a business (franchisee) obtains to get access to a business's secret knowledge, procedures, and trademarks to promote a product or provide services under the company's business name. The franchisee typically pays the franchisee an initial startup cost and yearly licensing fees in return for obtaining the franchise.
Recommended companies based on your search: