Why CUPS's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
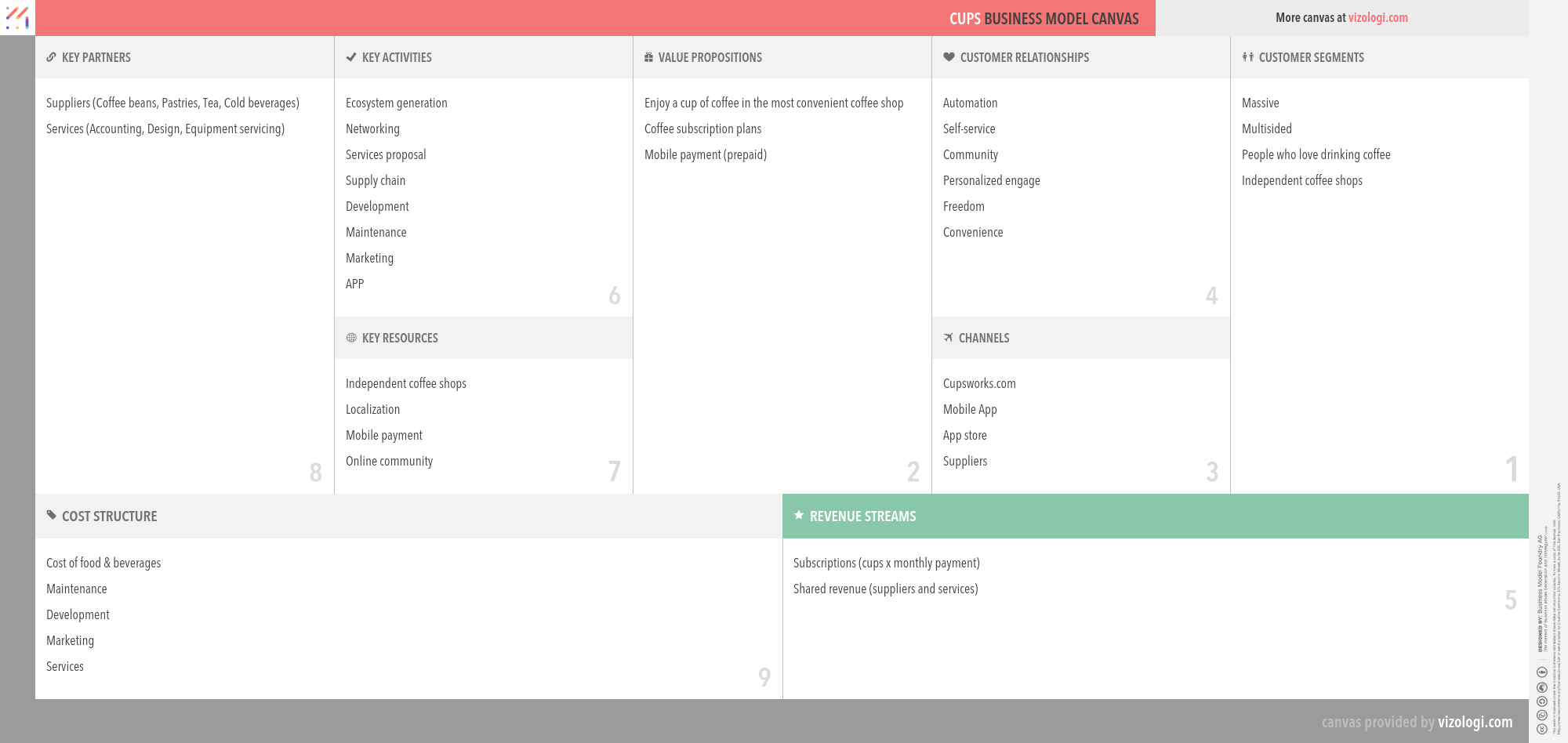
CUPS’s Company Overview
CUPS is a mobile app that was launched in New York City in April 2014. It acts as mobile payment and discovery platform for independent coffee shops. The app is currently active in more than 300 cafes in New York City, San Francisco, Philadelphia, and other US cities. Customers can use the app for individual transactions charged to a credit card, or purchase CUPS pre-paid “plans.”
https://cupsworks.comCountry: New York
Foundations date: 2012
Type: Private
Sector: Consumer Goods
Categories: Food & Beverages
CUPS’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: affiliation/belonging
Emotional: rewards me, therapeutic value, attractiveness, badge value, design/aesthetics
Functional: saves time, simplifies, connects, reduces effort, quality, variety, informs, sensory appeal, organizes, integrates
CUPS’s Related Competitors
CUPS’s Business Operations
Cross-selling:
Cross-selling is a business strategy in which additional services or goods are offered to the primary offering to attract new consumers and retain existing ones. Numerous businesses are increasingly diversifying their product lines with items that have little resemblance to their primary offerings. Walmart is one such example; they used to offer everything but food. They want their stores to function as one-stop shops. Thus, companies mitigate their reliance on particular items and increase overall sustainability by providing other goods and services.
Blue ocean strategy:
The blue ocean approach is predicated on the premise that market limits and industry structure are not predetermined and may be reconfigured via the actions and attitudes of industry participants. This is referred to as the reconstructionist perspective by the writers. Assuming that structure and market boundaries exist solely in managers' thoughts, practitioners who subscribe to this perspective avoid being constrained by actual market structures. To them, more demand exists, primarily untapped. The core of the issue is determining how to produce it.
Digitization:
This pattern is based on the capacity to convert current goods or services into digital versions, which have several benefits over intangible products, including increased accessibility and speed of distribution. In an ideal world, the digitalization of a product or service would occur without compromising the consumer value proposition. In other words, efficiency and multiplication achieved via digitalization do not detract from the consumer's perceived value. Being digitally sustainable encompasses all aspects of sustaining the institutional framework for developing and maintaining digital objects and resources and ensuring their long-term survival.
Aikido:
The aikido business model is often characterized as using a competitor's strength to get an edge over them. This is accomplished through finding weaknesses in a competitor's strategic position. In addition, it adds to marketing sustainability by exposing rivals' flaws, finding internal and external areas for development, and attracting consumers via specific product offers that deviate from the norm.
Digital:
A digital strategy is a strategic management and a business reaction or solution to a digital issue, which is often best handled as part of a broader company plan. A digital strategy is frequently defined by the application of new technologies to existing business activities and a focus on enabling new digital skills for their company (such as those formed by the Information Age and frequently as a result of advances in digital technologies such as computers, data, telecommunication services, and the World wide web, to name a few).
Corporate innovation:
Innovation is the outcome of collaborative creativity in turning an idea into a feasible concept, accompanied by a collaborative effort to bring that concept to life as a product, service, or process improvement. The digital era has created an environment conducive to business model innovation since technology has transformed how businesses operate and provide services to consumers.
Experience selling:
An experience in the sales model describes how a typical user perceives or comprehends a system's operation. A product or service's value is enhanced when an extra customer experience is included. Visual representations of experience models are abstract diagrams or metaphors derived from recognizable objects, actions, or systems. User interfaces use a range of experience models to help users rapidly comprehend what is occurring in the design, where they are, and what they may do next. For example, a software experience model may depict the connection between two applications and the relationship between an application and different navigation methods and other system or software components.
Ecosystem:
A business ecosystem is a collection of related entities ? suppliers, distributors, customers, rivals, and government agencies ? collaborating and providing a particular product or service. The concept is that each entity in the ecosystem influences and is impacted by the others, resulting in an ever-changing connection. Therefore, each entity must be adaptive and flexible to live, much like a biological ecosystem. These connections are often backed by a shared technical platform and are based on the flow of information, resources, and artifacts in the software ecosystem.
Mobile first behavior:
It is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices. The term is “mobile first,” and it is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices.
Open business:
Businesses use the open business approach to incorporate goods and services ecosystems from third parties that operate inside the same market framework. Collaboration between companies has the potential to increase the value delivered to the end customer or user. Software developers and platform integrators often use this business model.
Revenue sharing:
Revenue sharing occurs in various forms, but each iteration includes the sharing of operational gains or losses amongst connected financial players. Occasionally, revenue sharing is utilized as an incentive program ? for example, a small company owner may pay partners or colleagues a percentage-based commission for recommending new clients. Occasionally, revenue sharing is utilized to share the earnings generated by a corporate partnership.
Transaction facilitator:
The business acts as an acquirer, processing payments on behalf of online merchants, auction sites, and other commercial users for a fee. This encompasses all elements of purchasing, selling, and exchanging currencies at current or predetermined exchange rates. By far the biggest market in the world in terms of trade volume. The largest multinational banks are the leading players in this industry. Around the globe, financial hubs serve as anchors for trade between a diverse range of various kinds of buyers and sellers 24 hours a day, save on weekends.
Self-service:
A retail business model in which consumers self-serve the goods they want to buy. Self-service business concepts include self-service food buffets, self-service petrol stations, and self-service markets. Self-service is available through phone, online, and email to automate customer support interactions. Self-service Software and self-service applications (for example, online banking apps, shopping portals, and self-service check-in at airports) are becoming more prevalent.
Two-sided market:
Two-sided marketplaces, also called two-sided networks, are commercial platforms featuring two different user groups that mutually profit from the web. A multi-sided platform is an organization that generates value mainly via the facilitation of direct contacts between two (or more) distinct kinds of connected consumers (MSP). A two-sided market enables interactions between many interdependent consumer groups. The platform's value grows as more groups or individual members of each group use it. For example, eBay is a marketplace that links buyers and sellers. Google connects advertising and searchers. Social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook are also bidirectional, linking consumers and marketers.
Tradeable currency:
This pattern involves the creation of a digital asset and the establishment of a payment mechanism. Through this, the user earns points that may be used for other services.
Disruptive trends:
A disruptive technology supplants an existing technology and fundamentally alters an industry or a game-changing innovation that establishes an altogether new industry. Disruptive innovation is defined as an invention that shows a new market and value network and ultimately disrupts an established market and value network, replacing incumbent market-leading companies, products, and alliances.
Network builders:
This pattern is used to connecting individuals. It offers essential services for free but charges for extra services. The network effect is a paradox that occurs when more people utilize a product or service, the more valuable it becomes.
Experience:
Disrupts by offering a better understanding that customers are willing to pay for. Experience companies that have progressed may begin charging for the value of the transformation that an experience provides. An experienced company charges for the feelings consumers get as a result of their interaction with it.
Exposure:
This model collects data and connects it to others; it is suggested to investigate the impact of advertising on consumer purchase dynamics by explicitly linking the distribution of exposures from a brand's media schedule to the brand purchase incidence behavior patterns over time. The danger is that we may be unable to react productively and cost-effectively to technological and market changes.
Subscription:
Subscription business models are built on the concept of providing a product or service in exchange for recurring subscription income on a monthly or annual basis. As a result, they place a higher premium on client retention than on customer acquisition. Subscription business models, in essence, concentrate on revenue generation in such a manner that a single client makes repeated payments for extended access to a product or service. Cable television, internet providers, software suppliers, websites (e.g., blogs), business solutions providers, and financial services companies utilize this approach, as do conventional newspapers, periodicals, and academic publications.
Solution provider:
A solution provider consolidates all goods and services in a particular domain into a single point of contact. As a result, the client is supplied with a unique know-how to improve efficiency and performance. As a Solution Provider, a business may avoid revenue loss by broadening the scope of the service it offers, which adds value to the product. Additionally, close client interaction enables a better understanding of the customer's habits and requirements, enhancing goods and services.
Recommended companies based on your search: