Why Facebook's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
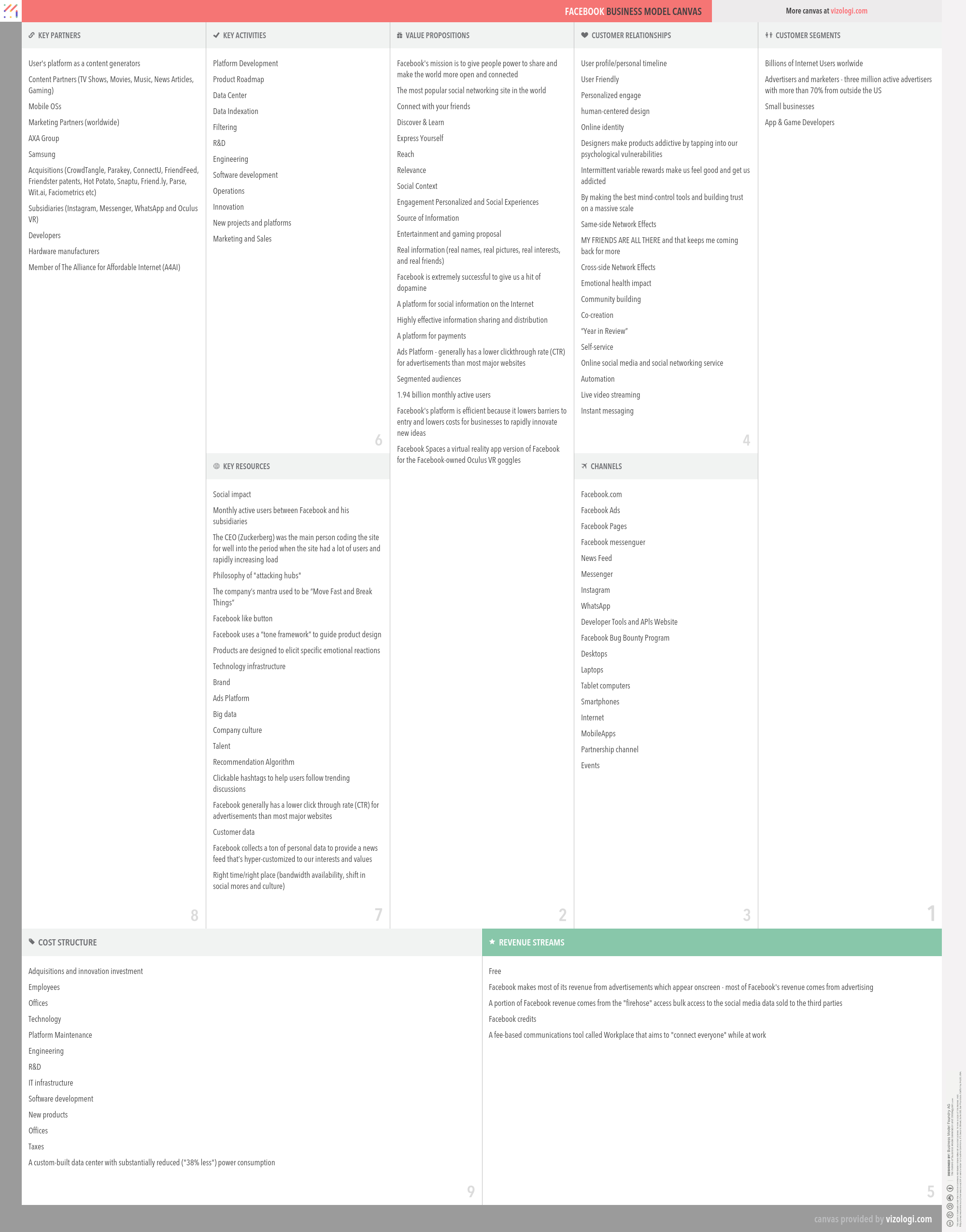
Facebook’s Company Overview
Facebook, Inc. builds products that enable people to connect and share through mobile devices and personal computers. The company enables people to share their opinions, ideas, photos and videos, and other activities. Its products include Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, WhatsApp, and Oculus. Facebook is a mobile application and website that enables people to connect, share, discover and communicate with each other on mobile devices and personal computers. Instagram is a mobile application that enables people to take photos or videos, customize them with filter effects, and share them with friends and followers in a photo feed or send them to friends. Messenger is a messaging application available for mobile and the Web on various platforms and devices. WhatsApp Messenger is a mobile messaging application that is used by people around the world. Oculus virtual reality technology and content platform allow people to play games, consume content and connect with others.
https://www.facebook.com/Country: California
Foundations date: 2004
Type: Public
Sector: Information & Media
Categories: Internet
Facebook’s Customer Needs
Social impact: self-transcendence
Life changing: provides hope, self-actualization, affiliation/belonging
Emotional: rewards me, badge value, fun/entertainment, attractiveness, provides access, design/aesthetics
Functional: organizes, connects, variety, informs, integrates, organizes, saves time, avoids hassles, sensory appeal, makes money
Facebook’s Related Competitors
Facebook’s Business Operations
Advertising:
This approach generated money by sending promotional marketing messages from other businesses to customers. When you establish a for-profit company, one of the most critical aspects of your strategy is determining how to generate income. Many companies sell either products or services or a mix of the two. However, advertisers are frequently the source of the majority of all of the revenue for online businesses and media organizations. This is referred to as an ad-based income model.
Affiliation:
Commissions are used in the affiliate revenue model example. Essentially, you resell goods from other merchants or businesses on your website or in your physical store. You are then compensated for referring new consumers to the company offering the goods or services. Affiliates often use a pay-per-sale or pay-per-display model. As a result, the business can access a more diversified prospective client base without extra active sales or marketing efforts. Affiliate marketing is a popular internet business strategy with significant potential for growth. When a client purchases via a referral link, the affiliate gets a portion of the transaction's cost.
Aikido:
The aikido business model is often characterized as using a competitor's strength to get an edge over them. This is accomplished through finding weaknesses in a competitor's strategic position. In addition, it adds to marketing sustainability by exposing rivals' flaws, finding internal and external areas for development, and attracting consumers via specific product offers that deviate from the norm.
Benchmarking services:
Benchmarking is a technique for evaluating performance and gaining insights via data analytics. It may be used to conduct internal research on your firm or compare it to other businesses to enhance business processes and performance indicators following best practices. Typically, three dimensions are measured: quality, time, and cost. In this manner, they may ascertain the targets' performance and, more significantly, the business processes that contribute to these companies' success. The digital transformation era has spawned a slew of data analysis-focused software businesses.
Blue ocean strategy:
The blue ocean approach is predicated on the premise that market limits and industry structure are not predetermined and may be reconfigured via the actions and attitudes of industry participants. This is referred to as the reconstructionist perspective by the writers. Assuming that structure and market boundaries exist solely in managers' thoughts, practitioners who subscribe to this perspective avoid being constrained by actual market structures. To them, more demand exists, primarily untapped. The core of the issue is determining how to produce it.
Collaborative production:
Producing goods in collaboration with customers based on their input, comments, naming, and price. It represents a new form of the socioeconomic output in which enormous individuals collaborate (usually over the internet). In general, initiatives based on the commons have less rigid hierarchical structures than those found on more conventional commercial models. However, sometimes not always?commons-based enterprises are structured so that contributors are not compensated financially.
Combining data within and across industries:
How can data from other sources be integrated to generate additional value? The science of big data, combined with emerging IT standards that enable improved data integration, enables new information coordination across businesses or sectors. As a result, intelligent executives across industries will see big data for what it is: a revolution in management. However, as with any other significant organizational transformation, the difficulties associated with becoming a big data-enabled company may be tremendous and require hands-on?or, in some instances, hands-off?leadership.
Community-funded:
The critical resource in this business strategy is a community's intellect. Three distinct consumer groups comprise this multifaceted business model: believers, suppliers, and purchasers. First, believers join the online community platform and contribute to the production of goods by vendors. Second, buyers purchase these goods, which may be visual, aural, or literary in nature. Finally, believers may be purchasers or providers, and vice versa.
Conversational commerce:
It is a reference to the nexus between chat applications and business. That is the trend toward engaging with organizations through messaging and chat applications such as Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, Talk, and WeChat, or via speech technologies like Amazon's Echo, allowing users to engage with businesses via voice commands.
Corporate innovation:
Innovation is the outcome of collaborative creativity in turning an idea into a feasible concept, accompanied by a collaborative effort to bring that concept to life as a product, service, or process improvement. The digital era has created an environment conducive to business model innovation since technology has transformed how businesses operate and provide services to consumers.
Cross-selling:
Cross-selling is a business strategy in which additional services or goods are offered to the primary offering to attract new consumers and retain existing ones. Numerous businesses are increasingly diversifying their product lines with items that have little resemblance to their primary offerings. Walmart is one such example; they used to offer everything but food. They want their stores to function as one-stop shops. Thus, companies mitigate their reliance on particular items and increase overall sustainability by providing other goods and services.
Cross-subsidiary:
When products and goods and products and services are integrated, they form a subsidiary side and a money side, maximizing the overall revenue impact. A subsidiary is a firm owned entirely or in part by another business, referred to as the parent company or holding company. A parent company with subsidiaries is a kind of conglomerate, a corporation that consists of several distinct companies; sometimes, the national or worldwide dispersion of the offices necessitates the establishment of subsidiaries.
Culture is brand:
It requires workers to live brand values to solve issues, make internal choices, and provide a branded consumer. Developing a distinctive and enduring cultural brand is the advertising industry's holy grail. Utilizing the hazy combination of time, attitude, and emotion to identify and replicate an ideology is near to marketing magic.
Curated retail:
Curated retail guarantees focused shopping and product relevance; it presents a consumer with the most appropriate options based on past purchases, interactions, and established preferences. It may be provided via human guidance, algorithmic recommendations, or a combination of the two.
Customer data:
It primarily offers free services to users, stores their personal information, and acts as a platform for users to interact with one another. Additional value is generated by gathering and processing consumer data in advantageous ways for internal use or transfer to interested third parties. Revenue is produced by either directly selling the data to outsiders or by leveraging it for internal reasons, such as increasing the efficacy of advertising. Thus, innovative, sustainable Big Data business models are as prevalent and desired as they are elusive (i.e., data is the new oil).
Channel aggregation:
Consolidating numerous distribution routes into one to achieve greater economic efficiency. A business model for internet commerce in which a company (that does not manufacture or warehouse any item) gathers (aggregates) information about products and services from many competing sources and displays it on its website. The firm's strength is in its power to create an 'environment' that attracts users to its website and develop a system that facilitates pricing and specification matching.
Data as a Service (DaaS):
Data as a Service (DaaS) is a relative of Software as a Service in computing (SaaS). As with other members of the as a service (aaS) family, DaaS is based on the idea that the product (in this instance, data) may be delivered to the user on-demand independent of the provider's geographic or organizational isolation from the customer. Additionally, with the advent[when?] of service-oriented architecture (SOA), the platform on which the data sits has become unimportant. This progression paved the way for the relatively recent new idea of DaaS to arise.
Digital:
A digital strategy is a strategic management and a business reaction or solution to a digital issue, which is often best handled as part of a broader company plan. A digital strategy is frequently defined by the application of new technologies to existing business activities and a focus on enabling new digital skills for their company (such as those formed by the Information Age and frequently as a result of advances in digital technologies such as computers, data, telecommunication services, and the World wide web, to name a few).
Digitization:
This pattern is based on the capacity to convert current goods or services into digital versions, which have several benefits over intangible products, including increased accessibility and speed of distribution. In an ideal world, the digitalization of a product or service would occur without compromising the consumer value proposition. In other words, efficiency and multiplication achieved via digitalization do not detract from the consumer's perceived value. Being digitally sustainable encompasses all aspects of sustaining the institutional framework for developing and maintaining digital objects and resources and ensuring their long-term survival.
Disruptive banking:
The banking industry's disruptors are changing the norms that have been in place for decades. These new regulations, however, will only be effective until the next round of disruption occurs. Banks and credit unions must thus be nimble and responsive. We need audacious tactics. 'Disruptive Innovation' is a term that refers to the process whereby a product or service establishes a foothold at the bottom of a market and then persistently climbs up the value chain, ultimately replacing existing rivals.
Disruptive trends:
A disruptive technology supplants an existing technology and fundamentally alters an industry or a game-changing innovation that establishes an altogether new industry. Disruptive innovation is defined as an invention that shows a new market and value network and ultimately disrupts an established market and value network, replacing incumbent market-leading companies, products, and alliances.
Ecosystem:
A business ecosystem is a collection of related entities ? suppliers, distributors, customers, rivals, and government agencies ? collaborating and providing a particular product or service. The concept is that each entity in the ecosystem influences and is impacted by the others, resulting in an ever-changing connection. Therefore, each entity must be adaptive and flexible to live, much like a biological ecosystem. These connections are often backed by a shared technical platform and are based on the flow of information, resources, and artifacts in the software ecosystem.
Exposure:
This model collects data and connects it to others; it is suggested to investigate the impact of advertising on consumer purchase dynamics by explicitly linking the distribution of exposures from a brand's media schedule to the brand purchase incidence behavior patterns over time. The danger is that we may be unable to react productively and cost-effectively to technological and market changes.
Fast fashion:
Fast fashion is a phrase fashion retailers use to describe how designs travel rapidly from the catwalk to catch current fashion trends. The emphasis is on optimizing specific supply chain components to enable these trends to be developed and produced quickly and affordably, allowing the mainstream customer to purchase current apparel designs at a reduced price.
Featured listings:
A highlighted listing is more important and noticeable than a regular listing, providing maximum exposure for your workplace to consumers searching in your region. In addition, customers are attracted to these premium listings because they include more pictures of your home ? and its excellent location.
Hidden revenue:
A hidden revenue business model is a revenue-generating strategy that excludes consumers from the equation, preventing them from paying for the service or product provided. For example, users of Google do not pay for the search engine. Rather than that, income streams are generated via advertising dollars spent by companies bidding on keywords.
Infomediary:
An infomediary acts as a personal agent for customers, assisting them to regain control over the information collected about them for marketing and advertising purposes. Infomediaries operate on the premise that personal data belongs to the individual represented, not necessarily the person who manages it.
Layer player:
Companies that add value across many markets and sectors are referred to be layer players. Occasionally, specialist companies achieve dominance in a specific niche market. The effectiveness of their operations, along with their economies of size and footprint, establish the business as a market leader.
Lead web:
Online lead generation is the technique of gathering or gaining a user's information ? often in return for an item, service, or information ? and then reselling that information to businesses interested in advertising to or selling to those gathering leads.
Long tail:
The long tail is a strategy that allows businesses to realize significant profit out of selling low volumes of hard-to-find items to many customers instead of only selling large volumes of a reduced number of popular items. The term was coined in 2004 by Chris Anderson, who argued that products in low demand or with low sales volume can collectively make up market share that rivals or exceeds the relatively few current bestsellers and blockbusters but only if the store or distribution channel is large enough.
Markets are conversations:
For professional services firms, the difference will be made by converting non-engaged customers into engaged customers. Product development will be obsolete. Customer relations and conversations will replace it. By sharing modular and beta products and services with your current and future customers, companies and their customers interact and collaborate in ongoing conversations. Not only will customers find and follow companies in online social networks, but it will also be the other way around as well.
Mobile first behavior:
It is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices. The term is “mobile first,” and it is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices.
Network builders:
This pattern is used to connecting individuals. It offers essential services for free but charges for extra services. The network effect is a paradox that occurs when more people utilize a product or service, the more valuable it becomes.
Power on:
This method allows the modification of current structures via the use of cutting-edge technology, as shown by growing political unrest, a crisis in representation and governance, and upstart companies upending established sectors. Nevertheless, the nature of this transition is often exaggerated or severely underestimated. As a result, some cling to delirious fantasies of a new techno-utopia in which greater connection results in direct democracy and wealth.
Product innovation:
Product innovation is the process of developing and introducing a new or better version of an existing product or service. This is a broader definition of innovation than the generally recognized definition, which includes creating new goods that are considered innovative in this context. For example, Apple launched a succession of successful new products and services in 2001?the iPod, the iTunes online music service, and the iPhone?which catapulted the firm to the top of its industry.
Referral:
Referral marketing is a technique for acquiring new consumers by advertising goods or services through recommendations or ordinary word of mouth. While these recommendations often occur spontaneously, companies may influence this via the use of suitable tactics. Referral marketing is a technique for increasing referrals through word of mouth, arguably the oldest and most trusted kind of marketing. This may be done by incentivizing and rewarding consumers. A diverse range of other contacts to suggest goods and services from consumer and business-to-business companies, both online and offline.
Reputation builders:
Reputation builders is an innovative software platform that enables companies to create, collect, and manage positive internet reviews. It was a pioneer in the utilization of user-generated material. The website services are provided for free to users, who supply the majority of the content, and the websites of related businesses are monetized via advertising.
Self-service:
A retail business model in which consumers self-serve the goods they want to buy. Self-service business concepts include self-service food buffets, self-service petrol stations, and self-service markets. Self-service is available through phone, online, and email to automate customer support interactions. Self-service Software and self-service applications (for example, online banking apps, shopping portals, and self-service check-in at airports) are becoming more prevalent.
Skunkworks project:
A skunkworks project is one that is created by a small, loosely organized group of individuals who study and develop a project with the primary goal of radical innovation. The terminology arose during World War II with Lockheed's Skunk Works project. However, since its inception with Skunk Works, the phrase has been used to refer to comparable high-priority research and development initiatives at other big companies that include a small team operating outside of their regular working environment and free of managerial restrictions. Typically, the phrase alludes to semi-secretive technological initiatives, such as Google X Lab.
Sponsorship:
In most instances, support is not intended to be philanthropic; instead, it is a mutually beneficial commercial relationship. In the highly competitive sponsorship climate of sport, a business aligning its brand with a mark seeks a variety of economic, public relations, and product placement benefits. Sponsors also seek to establish public trust, acceptability, or alignment with the perceived image a sport has built or acquired by leveraging their connection with an athlete, team, league, or the sport itself.
Tag management:
Tag management refers to the capability of the collaborative software to handle both your own and user-generated tags. Marketers use various third-party solutions to enhance their websites, video content, and mobile applications. Web analytics, campaign analytics, audience measurement, customization, A/B testing, ad servers, retargeting, and conversion tracking are examples of such systems. At its most fundamental level, tag management enables new methods for your business model to use data.
Take the wheel:
Historically, the fundamental principles for generating and extracting economic value were rigorous. Businesses attempted to implement the same business concepts more effectively than their rivals. New sources of sustained competitive advantage are often only accessible via business model reinvention driven by disruptive innovation rather than incremental change or continuous improvement.
Technology trends:
New technologies that are now being created or produced in the next five to ten years will significantly change the economic and social landscape. These include but are not limited to information technology, wireless data transmission, human-machine connection, on-demand printing, biotechnology, and sophisticated robotics.
Trading data:
Combining disparate data sets enables businesses to develop a variety of new offerings for complementary companies. Robustness is a property that describes a model's, test's, or system's ability to perform effectively when its variables or assumptions are changed, ensuring that a robust concept operates without fail under various conditions. In general, robustness refers to a system's capacity to deal with unpredictability while remaining practical.
Two-sided market:
Two-sided marketplaces, also called two-sided networks, are commercial platforms featuring two different user groups that mutually profit from the web. A multi-sided platform is an organization that generates value mainly via the facilitation of direct contacts between two (or more) distinct kinds of connected consumers (MSP). A two-sided market enables interactions between many interdependent consumer groups. The platform's value grows as more groups or individual members of each group use it. For example, eBay is a marketplace that links buyers and sellers. Google connects advertising and searchers. Social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook are also bidirectional, linking consumers and marketers.
Unlimited niches:
Online retailers provide specialized content to various niche client groups via continuing mass-customized customer relationships. The sector of technical content providers is a second client segment. Combining these two factors may result in an infinite number of niches. New material is produced and distributed through online channels, which implies that online retailers must prioritize platform maintenance and marketing in addition to service delivery.
User design:
A client is both the manufacturer and the consumer in user manufacturing. For instance, an online platform could offer the client the tools required to create and market the product, such as product design software, manufacturing services, or an online store to sell the goods. In addition, numerous software solutions enable users to create and customize their products to respond to changing consumer requirements seamlessly.
Virtual reality:
AR/VR is the fourth significant platform change (after PC, web, and mobile). First, CEOs must choose how to play. Business models are determined by installed bases, use cases, and unit economics; there is no one-size-fits-all answer; each situation is unique, and developers must do market research and analysis before making a choice. Relying on advertising-income is a handy strategy for unknown businesses or newcomers to the market. It allows them to use their prior expertise with mobile and online ad campaigns.
Recommended companies based on your search: