Why Instacart's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
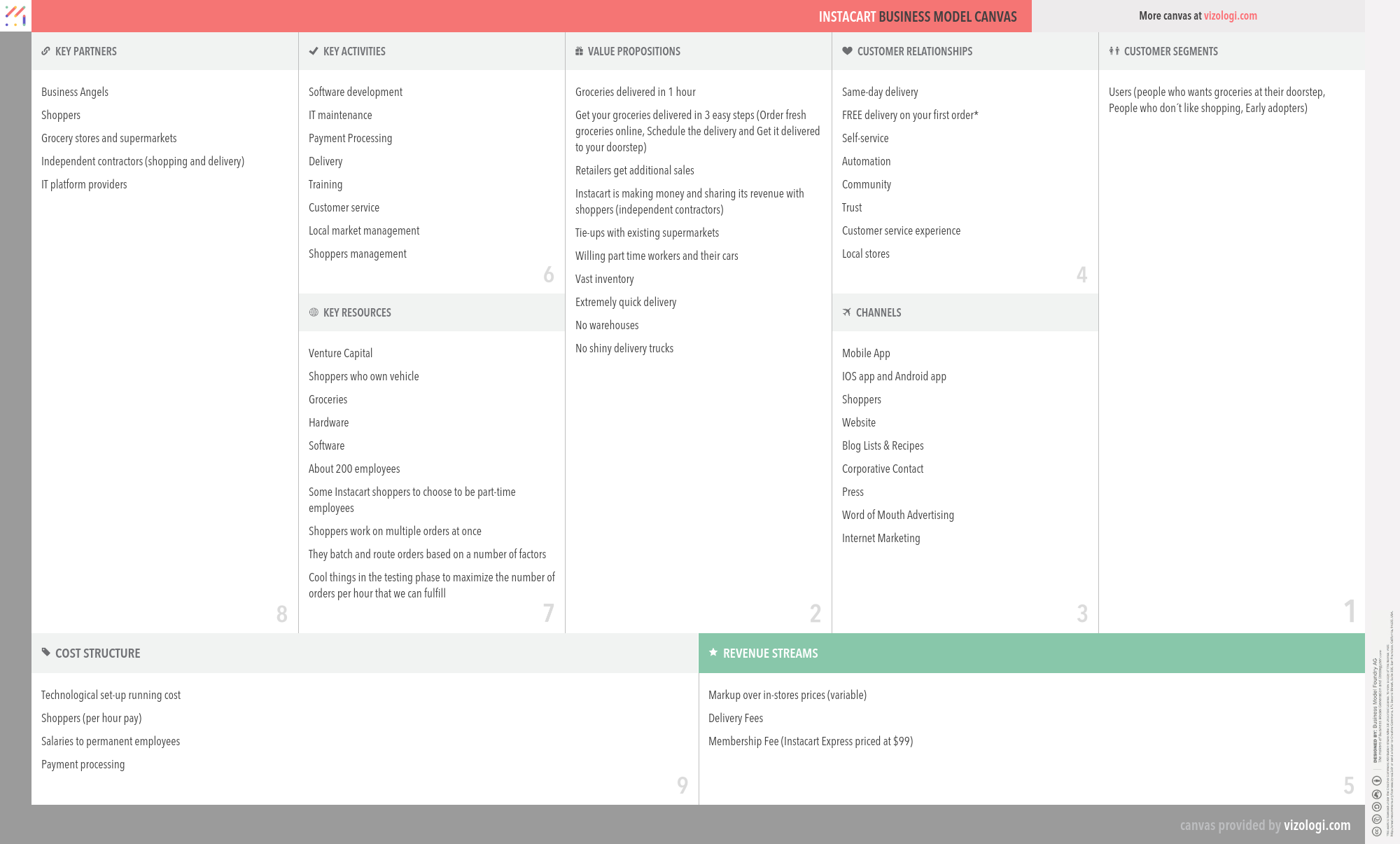
Instacart’s Company Overview
Instacart is a same-day grocery delivery startup offering delivery in as little as one hour. Focused on delivering groceries and home essentials, Instacart already has over 500.000 items from local stores in its catalog.
https://www.instacart.com/Instacart’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: affiliation/belonging
Emotional: reduces anxiety, rewards me, badge value, provides access
Functional: saves time, simplifies, connects, reduces effort, quality, variety, sensory appeal, integrates, organizes
Instacart’s Related Competitors
Instacart’s Business Operations
Codifying a distinctive service capability:
Since their inception, information technology systems have aided in automating corporate operations, increasing productivity, and maximizing efficiency. Now, businesses can take their perfected processes, standardize them, and sell them to other parties. In today's corporate environment, innovation is critical for survival.
Digital transformation:
Digitalization is the systematic and accelerated transformation of company operations, processes, skills, and models to fully exploit the changes and possibilities brought about by digital technology and its effect on society. Digital transformation is a journey with many interconnected intermediate objectives, with the ultimate aim of continuous enhancement of processes, divisions, and the business ecosystem in a hyperconnected age. Therefore, establishing the appropriate bridges for the trip is critical to success.
Dynamic pricing:
This pattern allows the business to adjust its rates in response to national or regional trends. Dynamic pricing is a pricing technique known as surge pricing, demand pricing, or time-based pricing. In which companies establish variable prices for their goods or services in response to changing market conditions. Companies may adjust their rates based on algorithms that consider rival pricing, supply and demand, and other market variables. Dynamic pricing is widely used in various sectors, including hospitality, travel, entertainment, retail, energy, and public transportation.
Experience selling:
An experience in the sales model describes how a typical user perceives or comprehends a system's operation. A product or service's value is enhanced when an extra customer experience is included. Visual representations of experience models are abstract diagrams or metaphors derived from recognizable objects, actions, or systems. User interfaces use a range of experience models to help users rapidly comprehend what is occurring in the design, where they are, and what they may do next. For example, a software experience model may depict the connection between two applications and the relationship between an application and different navigation methods and other system or software components.
Lean Start-up:
The Lean Start-up methodology is a scientific approach to developing and managing businesses that focuses on getting the desired product into consumers' hands as quickly as possible. The Lean Startup method coaches you on how to guide a startup?when to turn, when to persevere?and how to build a company with maximum acceleration. It is a guiding philosophy for new product development.
Membership club:
Belonging to a group, either individually or collectively. Certain memberships may charge a fee to join or participate, while others are free. Others have particular skill criteria that must be met before membership is granted. Members are entitled to specific benefits or advantages, but not all members may enjoy the same rights and privileges. Another method is taken by a members-only luxury lifestyle management business that offers concierge services such as vacation reservations, restaurant suggestions, and event access.
Mobile first behavior:
It is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices. The term is “mobile first,” and it is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices.
On-demand economy:
The on-demand economy is described as economic activity generated by digital marketplaces that meet customer demand for products and services via quick access and accessible supply. The supply chain is managed via a highly efficient, intuitive digital mesh built on top of current infrastructure networks. The on-demand economy is transforming commercial behavior in cities worldwide. The number of businesses, the categories covered, and the industry's growth rate are all increasing. Businesses in this new economy are the culmination of years of technological progress and customer behavior change.
Online marketplace:
An online marketplace (or online e-commerce marketplace) is a kind of e-commerce website in which product or service information is supplied by various third parties or, in some instances, the brand itself, while the marketplace operator handles transactions. Additionally, this pattern encompasses peer-to-peer (P2P) e-commerce between businesses or people. By and large, since marketplaces aggregate goods from a diverse range of suppliers, the variety and availability are typically greater than in vendor-specific online retail shops. Additionally, pricing might be more competitive.
Revenue sharing:
Revenue sharing occurs in various forms, but each iteration includes the sharing of operational gains or losses amongst connected financial players. Occasionally, revenue sharing is utilized as an incentive program ? for example, a small company owner may pay partners or colleagues a percentage-based commission for recommending new clients. Occasionally, revenue sharing is utilized to share the earnings generated by a corporate partnership.
Sharing economy:
The sharing economy eliminates the necessity for individual asset ownership. The phrase sharing economy is an umbrella word that encompasses various definitions and is often used to refer to economic and social activity that involves online transactions. Originally coined by the open-source community to refer to peer-to-peer sharing of access to goods and services, the term is now occasionally used more broadly to refer to any sales transaction conducted via online marketplaces, including those that are business to consumer (B2C) than peer-to-peer.
Subscription:
Subscription business models are built on the concept of providing a product or service in exchange for recurring subscription income on a monthly or annual basis. As a result, they place a higher premium on client retention than on customer acquisition. Subscription business models, in essence, concentrate on revenue generation in such a manner that a single client makes repeated payments for extended access to a product or service. Cable television, internet providers, software suppliers, websites (e.g., blogs), business solutions providers, and financial services companies utilize this approach, as do conventional newspapers, periodicals, and academic publications.
Supermarket:
A supermarket is a self-service store arranged into aisles and has many foods and home goods. It is bigger and has a greater variety than traditional grocery shops but is smaller and offers a more limited selection than a hypermarket or big-box market. Supermarkets are usually chain shops supplied by their parent firms' distribution centers, allowing for more significant economies of scale. In addition, supermarkets often provide items at competitive rates by using their purchasing power to negotiate lower pricing from producers than smaller shops can.
Two-sided market:
Two-sided marketplaces, also called two-sided networks, are commercial platforms featuring two different user groups that mutually profit from the web. A multi-sided platform is an organization that generates value mainly via the facilitation of direct contacts between two (or more) distinct kinds of connected consumers (MSP). A two-sided market enables interactions between many interdependent consumer groups. The platform's value grows as more groups or individual members of each group use it. For example, eBay is a marketplace that links buyers and sellers. Google connects advertising and searchers. Social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook are also bidirectional, linking consumers and marketers.
Uberization:
Uberization is a phrase that refers to a shift to an operational paradigm that allows economic actors to trade underused capacity of existing assets or human resources at near-zero transaction costs. The word Uberization is taken from the company's name. Thus, the model's operational expenses are distinct from those of an established company.
Recommended companies based on your search: