Why M-Pesa's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
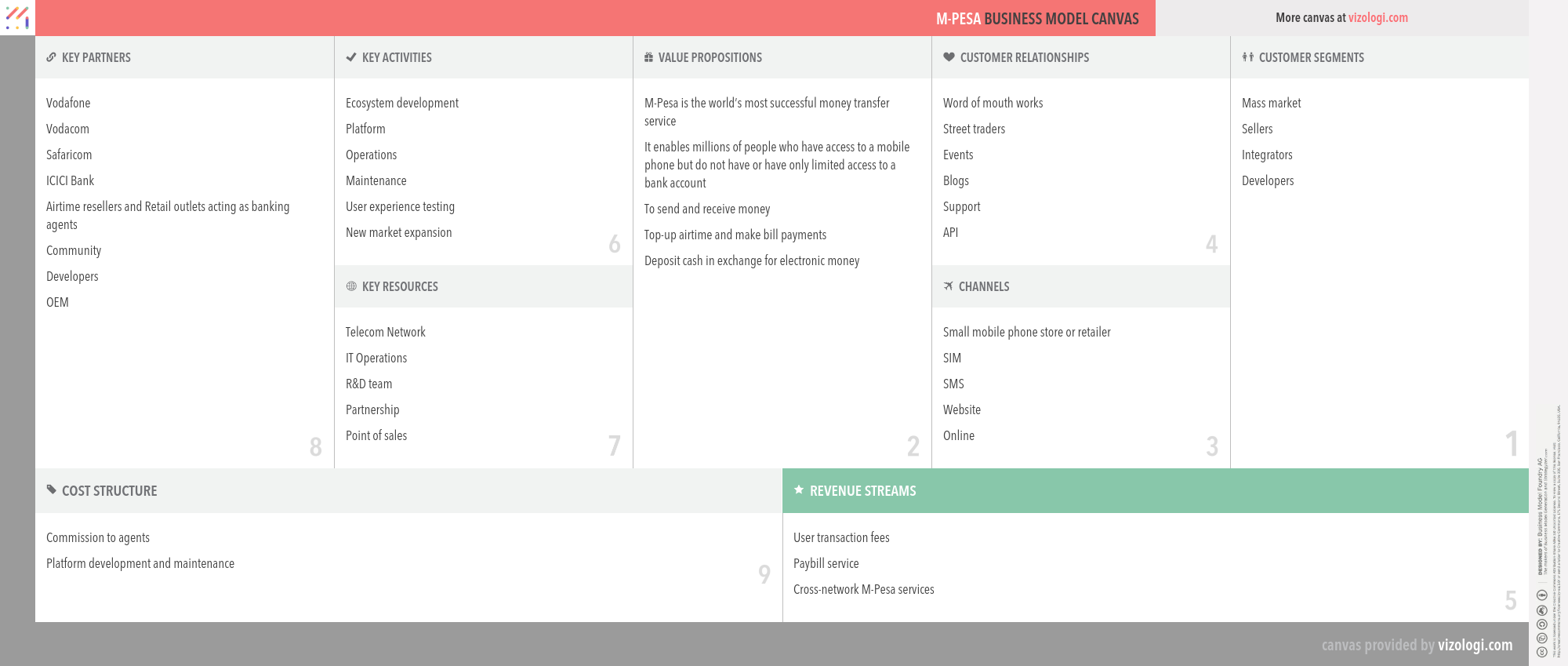
M-Pesa’s Company Overview
M-Pesa is a mobile phone-based money transfer, financing and microfinancing service, launched in 2007 by Vodafone for Safaricom and Vodacom, the largest mobile network operators in Kenya and Tanzania.
https://www.mpesa.inCountry: Kenya
Foundations date: 2007
Type: Subsidiary
Sector: Financials
Categories: Financial Services
M-Pesa’s Customer Needs
Social impact: self-transcendence
Life changing: self-actualization, provides hope, affiliation/belonging
Emotional: reduces anxiety, rewards me, attractiveness, provides access
Functional: saves times, simplifies, makes money, integrates, connects, reduces effort, avoid hassles, organizes, avoids hassles
M-Pesa’s Related Competitors
M-Pesa’s Business Operations
Aikido:
The aikido business model is often characterized as using a competitor's strength to get an edge over them. This is accomplished through finding weaknesses in a competitor's strategic position. In addition, it adds to marketing sustainability by exposing rivals' flaws, finding internal and external areas for development, and attracting consumers via specific product offers that deviate from the norm.
Alternative currencies and banking:
Alternative currencies (also known as private currencies) are units of value issued by a private entity, such as a business or a non-profit organization. A private company or organization usually produces a private currency to serve as an alternative to a national or fiat currency, usually the country's standard unit of value. For example, mutual credit is a kind of alternative currency, and therefore any loan that does not go via the banking system qualifies as an alternative currency.
Blended value:
Blended value is a relatively new conceptual framework in which non-profit organizations, companies, and investments are assessed on their capacity to create a combination of financial, social, and environmental value. Businesses that use mixed value business models actively enhance their social impact while maintaining economic efficiency. A fair-trade coffee cooperative, for example, generates social value via guaranteed minimum prices given to coffee growers and direct investments in community development.
Brokerage:
A brokerage firm's primary responsibility is to serve as a middleman, connecting buyers and sellers to complete transactions. Accordingly, brokerage firms are compensated through commission once a transaction is completed. For example, when a stock trade order is executed, a transaction fee is paid by an investor to repay the brokerage firm for its efforts in completing the transaction.
Cash machine:
The cash machine business model allows companies to obtain money from sales since consumers pay ahead for the goods they purchase, but the costs required to generate the revenue are not yet paid. This increases companies' liquidity, which they may use to pay off debt or make additional investments. Among several others, the online store Amazon often employs this business model.
Cashier-as-a-service:
Cashier-as-a-Service (CaaS) describes the practice of paying using a third-party service. When consumers purchase goods online, they often pay the seller indirectly via a third party - the cashier. Both the consumer and the merchant place their confidence in the cashier, who is supposed to facilitate the trustworthy and safe transfer of money. By paying a business through a cashier, consumers may purchase goods without providing merchants with their financial data.
Disruptive banking:
The banking industry's disruptors are changing the norms that have been in place for decades. These new regulations, however, will only be effective until the next round of disruption occurs. Banks and credit unions must thus be nimble and responsive. We need audacious tactics. 'Disruptive Innovation' is a term that refers to the process whereby a product or service establishes a foothold at the bottom of a market and then persistently climbs up the value chain, ultimately replacing existing rivals.
Disruptive trends:
A disruptive technology supplants an existing technology and fundamentally alters an industry or a game-changing innovation that establishes an altogether new industry. Disruptive innovation is defined as an invention that shows a new market and value network and ultimately disrupts an established market and value network, replacing incumbent market-leading companies, products, and alliances.
Easy and low cost money transfer and payment:
This business model makes cheaper and more accessible for users to transfer money and make and collect payments. Sending or receiving money for either payment of salaries, settlement of business transactions, payment of school fees, or for family support is common both for businesses and individuals. It requires efficient, reliable and affordable money transfer services whereby money can be deposited in one location and withdrawn in another in both urban and rural areas.
Ecosystem:
A business ecosystem is a collection of related entities ? suppliers, distributors, customers, rivals, and government agencies ? collaborating and providing a particular product or service. The concept is that each entity in the ecosystem influences and is impacted by the others, resulting in an ever-changing connection. Therefore, each entity must be adaptive and flexible to live, much like a biological ecosystem. These connections are often backed by a shared technical platform and are based on the flow of information, resources, and artifacts in the software ecosystem.
Layer player:
Companies that add value across many markets and sectors are referred to be layer players. Occasionally, specialist companies achieve dominance in a specific niche market. The effectiveness of their operations, along with their economies of size and footprint, establish the business as a market leader.
Microfinance:
Microfinance provides financial services to entrepreneurs and small companies who may not access traditional banking and financial services. The two primary delivery methods for financial services to such customers are (1) relationship-based banking for individuals and small companies and (2) group-based models, in which many entrepreneurs pool their resources to apply for loans and other services together.
Microfranchising:
Microfranchising is a business model that applies elements and concepts of traditional franchising to small businesses in the developing world. It refers to the systemization and replication of micro-enterprises. Microfranchising is broadly defined as small businesses that can easily be replicated by following proven marketing and operational concepts.
Micropayment:
Micropayments are financial transactions involving a tiny amount of money that is frequently conducted online. While micropayments were initially intended to apply minimal amounts of money, practical systems allowing less than one dollar transactions have met with little success. One impediment to the development of micropayment systems has been the need to keep transaction costs low, which is impracticable when transferring such tiny amounts, even if the transaction charge is just a few cents.
Mobile first behavior:
It is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices. The term is “mobile first,” and it is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices.
Private level banking:
Private label banks allow any business with a sizable client base, brand, or unique technological solution to operating as a private label bank. Private banking refers to the customized financial and banking services to its affluent high net worth individual (HNWI) customers. HNWIs generally have more money than ordinary individuals, enabling them to access a broader range of conventional and alternative assets. Private banks' goal is to connect such people with the most suitable alternatives.
Robin Hood:
They 'rob' the wealthy and give to the needy, which distinguishes them from their main competitor, who does the polar opposite. Products and services are used by 'the poor' for a low or even no cost, while 'the wealthy' pay a more fantastic price. In addition, it contributes to brand recognition and makes 'the wealthy' feel better about purchasing since it benefits impoverished people. The most outstanding example is TOMS Shoes, which gives one pair of shoes to a kid in need for every couple sold to customers.
Self-service:
A retail business model in which consumers self-serve the goods they want to buy. Self-service business concepts include self-service food buffets, self-service petrol stations, and self-service markets. Self-service is available through phone, online, and email to automate customer support interactions. Self-service Software and self-service applications (for example, online banking apps, shopping portals, and self-service check-in at airports) are becoming more prevalent.
Social stakeholder:
Social responsibility will only be accurate if many managers embrace moral leadership rather than immoral leadership, organizational management, and business ethics that engage morals and values in corporate governance. In a nutshell, it addresses the concept of who or what really matters.
Target the poor:
The product or service provided here is aimed towards the bottom of the pyramid rather than the top. The target of the flawed business model is a financially feasible strategy that helps low-income communities by integrating them in the value chain of a firm on the demand side as customers and consumers and the supply side as producers, entrepreneurs, or workers in a sustainable manner. While the business earns a little profit on each product sold, it profits from the increased sales volume often associated with a large client base.
Tradeable currency:
This pattern involves the creation of a digital asset and the establishment of a payment mechanism. Through this, the user earns points that may be used for other services.
Transaction facilitator:
The business acts as an acquirer, processing payments on behalf of online merchants, auction sites, and other commercial users for a fee. This encompasses all elements of purchasing, selling, and exchanging currencies at current or predetermined exchange rates. By far the biggest market in the world in terms of trade volume. The largest multinational banks are the leading players in this industry. Around the globe, financial hubs serve as anchors for trade between a diverse range of various kinds of buyers and sellers 24 hours a day, save on weekends.
Recommended companies based on your search: