Why Outbrain's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
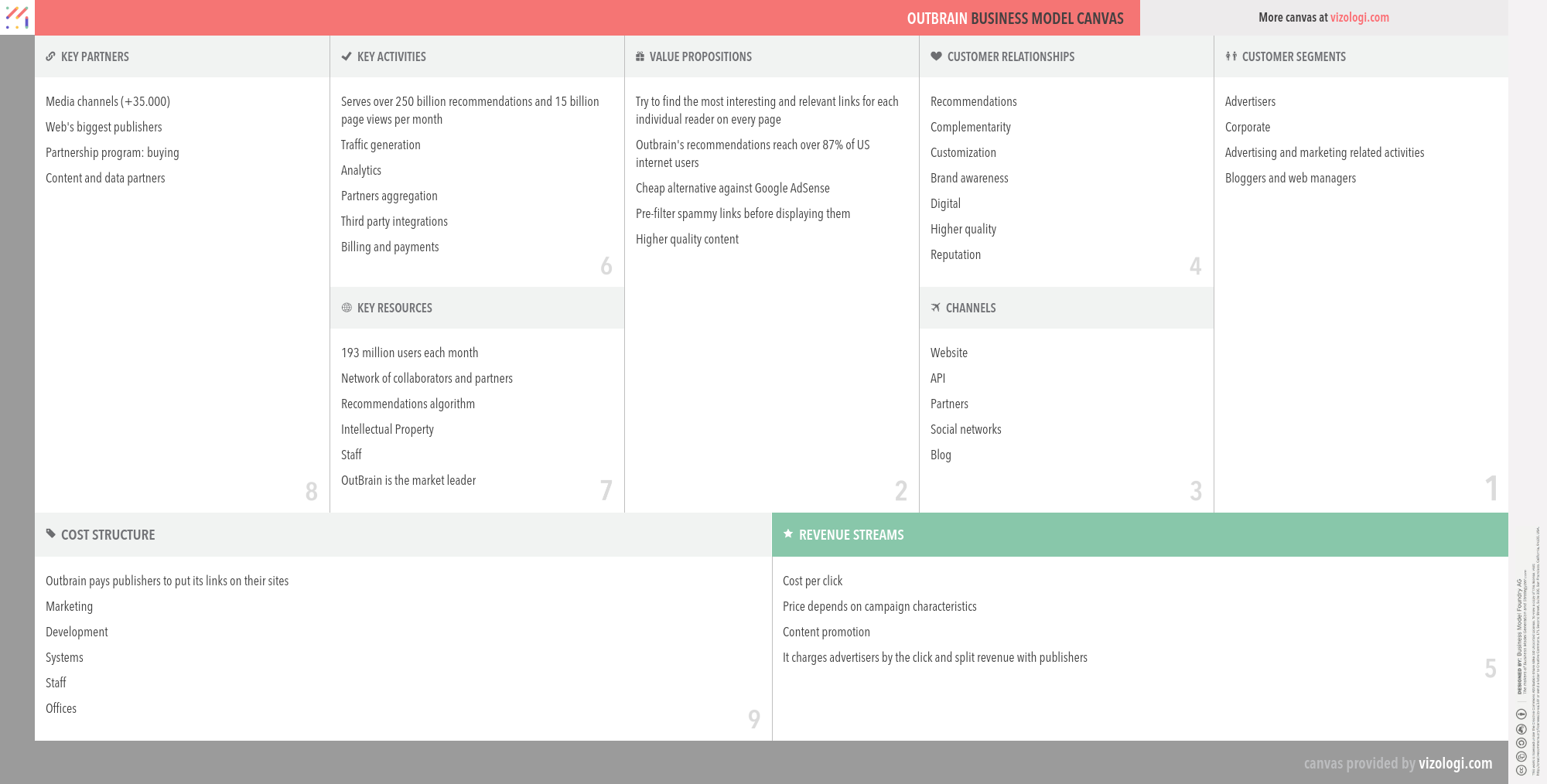
Outbrain’s Company Overview
Outbrain is the leading content discovery platform, reaching a highly engaged audience through distribution on top publisher sites. Outbrain provides publishers a service for recommended links to increase traffic and generate revenue. Outbrain also works with brands and agencies, offering a way to distribute content alongside publisher's own editorial recommendations.
http://www.outbrain.com/Country: Israel
Foundations date: 2006
Type: Private
Sector: Information & Media
Categories: Advertising
Outbrain’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: affiliation/belonging, self-actualization
Emotional: provides access, badge value
Functional: makes money, reduces effort, reduces costs, integrates, connects, reduces effort
Outbrain’s Related Competitors
Outbrain’s Business Operations
Acquiring non customers:
Acquiring non customers who traditionally did not seem to be the target of customer value proposition. Customer acquisition refers to gaining new consumers. Acquiring new customers involves persuading consumers to purchase a company’s products and/or services. Companies and organizations consider the cost of customer acquisition as an important measure in evaluating how much value customers bring to their businesses.
Advertising:
This approach generated money by sending promotional marketing messages from other businesses to customers. When you establish a for-profit company, one of the most critical aspects of your strategy is determining how to generate income. Many companies sell either products or services or a mix of the two. However, advertisers are frequently the source of the majority of all of the revenue for online businesses and media organizations. This is referred to as an ad-based income model.
Codifying a distinctive service capability:
Since their inception, information technology systems have aided in automating corporate operations, increasing productivity, and maximizing efficiency. Now, businesses can take their perfected processes, standardize them, and sell them to other parties. In today's corporate environment, innovation is critical for survival.
Digital:
A digital strategy is a strategic management and a business reaction or solution to a digital issue, which is often best handled as part of a broader company plan. A digital strategy is frequently defined by the application of new technologies to existing business activities and a focus on enabling new digital skills for their company (such as those formed by the Information Age and frequently as a result of advances in digital technologies such as computers, data, telecommunication services, and the World wide web, to name a few).
Disintermediation:
Keeping the purchase price low by avoiding mediators and maximizing supply margins is a win-win situation. In finance, disintermediation refers to how money is removed from intermediate financial organizations such as banks and savings and loan associations and invested directly. Disintermediation, in general, refers to the process of eliminating the middleman or intermediary from future transactions. Disintermediation is often used to invest in higher-yielding securities.
Dynamic pricing:
This pattern allows the business to adjust its rates in response to national or regional trends. Dynamic pricing is a pricing technique known as surge pricing, demand pricing, or time-based pricing. In which companies establish variable prices for their goods or services in response to changing market conditions. Companies may adjust their rates based on algorithms that consider rival pricing, supply and demand, and other market variables. Dynamic pricing is widely used in various sectors, including hospitality, travel, entertainment, retail, energy, and public transportation.
Exposure:
This model collects data and connects it to others; it is suggested to investigate the impact of advertising on consumer purchase dynamics by explicitly linking the distribution of exposures from a brand's media schedule to the brand purchase incidence behavior patterns over time. The danger is that we may be unable to react productively and cost-effectively to technological and market changes.
Lead web:
Online lead generation is the technique of gathering or gaining a user's information ? often in return for an item, service, or information ? and then reselling that information to businesses interested in advertising to or selling to those gathering leads.
Markets are conversations:
For professional services firms, the difference will be made by converting non-engaged customers into engaged customers. Product development will be obsolete. Customer relations and conversations will replace it. By sharing modular and beta products and services with your current and future customers, companies and their customers interact and collaborate in ongoing conversations. Not only will customers find and follow companies in online social networks, but it will also be the other way around as well.
Micro-segmentation:
Micro-segmentation is a more sophisticated type of segmentation in which a small number of consumers are classified into very accurate categories based on various variables, including behavioral forecasts. Customer micro-segmentation is the process of segmenting a firm's customers into groups based on their relationship with that business. The purpose of segmenting customers is to determine how to relate to each segment's customers to optimize each customer's value to the company.
Product innovation:
Product innovation is the process of developing and introducing a new or better version of an existing product or service. This is a broader definition of innovation than the generally recognized definition, which includes creating new goods that are considered innovative in this context. For example, Apple launched a succession of successful new products and services in 2001?the iPod, the iTunes online music service, and the iPhone?which catapulted the firm to the top of its industry.
Revenue sharing:
Revenue sharing occurs in various forms, but each iteration includes the sharing of operational gains or losses amongst connected financial players. Occasionally, revenue sharing is utilized as an incentive program ? for example, a small company owner may pay partners or colleagues a percentage-based commission for recommending new clients. Occasionally, revenue sharing is utilized to share the earnings generated by a corporate partnership.
Self-service:
A retail business model in which consumers self-serve the goods they want to buy. Self-service business concepts include self-service food buffets, self-service petrol stations, and self-service markets. Self-service is available through phone, online, and email to automate customer support interactions. Self-service Software and self-service applications (for example, online banking apps, shopping portals, and self-service check-in at airports) are becoming more prevalent.
Take the wheel:
Historically, the fundamental principles for generating and extracting economic value were rigorous. Businesses attempted to implement the same business concepts more effectively than their rivals. New sources of sustained competitive advantage are often only accessible via business model reinvention driven by disruptive innovation rather than incremental change or continuous improvement.
Recommended companies based on your search: