Why Subway's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
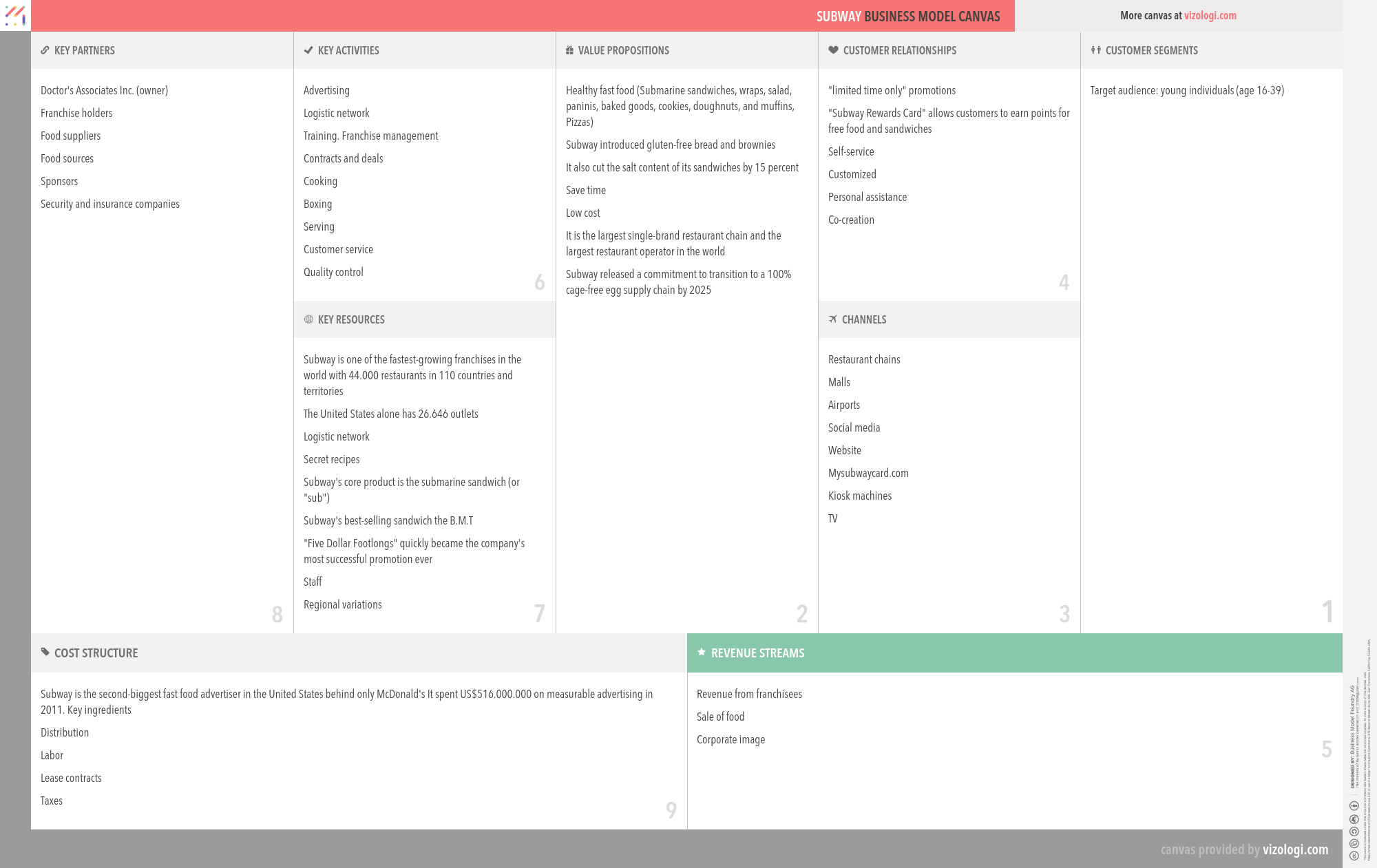
Subway’s Company Overview
SUBWAY is an American fast food restaurant franchise that primarily sells submarine sandwiches (subs) and salads. Its menu includes a wide selection of sandwiches, salads, breakfasts, desserts, cookies, and beverages.
www.subway.comCountry: Connecticut
Foundations date: 1978
Type: Subsidiary
Sector: Consumer Goods
Categories: Restaurants
Subway’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: affiliation/belonging
Emotional: reduces anxiety, fun/entertainment, badge value, design/aesthetics, rewards me
Functional: saves time, simplifies, avoids hassles, reduces cost, sensory appeal
Subway’s Related Competitors
Subway’s Business Operations
Affiliation:
Commissions are used in the affiliate revenue model example. Essentially, you resell goods from other merchants or businesses on your website or in your physical store. You are then compensated for referring new consumers to the company offering the goods or services. Affiliates often use a pay-per-sale or pay-per-display model. As a result, the business can access a more diversified prospective client base without extra active sales or marketing efforts. Affiliate marketing is a popular internet business strategy with significant potential for growth. When a client purchases via a referral link, the affiliate gets a portion of the transaction's cost.
Bundling:
Multiple products or services have been bundled together to enhance the value. Bundling is a marketing technique in which goods or services are bundled to be sold as a single entity. Bundling enables the purchasing of several goods and services from a single vendor. While the goods and services are often linked, they may also consist of different items that appeal to a particular market segment.
Cross-selling:
Cross-selling is a business strategy in which additional services or goods are offered to the primary offering to attract new consumers and retain existing ones. Numerous businesses are increasingly diversifying their product lines with items that have little resemblance to their primary offerings. Walmart is one such example; they used to offer everything but food. They want their stores to function as one-stop shops. Thus, companies mitigate their reliance on particular items and increase overall sustainability by providing other goods and services.
Customer loyalty:
Customer loyalty is a very successful business strategy. It entails giving consumers value that extends beyond the product or service itself. It is often provided through incentive-based programs such as member discounts, coupons, birthday discounts, and points. Today, most businesses have some kind of incentive-based programs, such as American Airlines, which rewards customers with points for each trip they take with them.
Direct selling:
Direct selling refers to a situation in which a company's goods are immediately accessible from the manufacturer or service provider rather than via intermediate channels. The business avoids the retail margin and any extra expenses connected with the intermediaries in this manner. These savings may be passed on to the client, establishing a consistent sales experience. Furthermore, such intimate touch may help to strengthen client connections. Finally, direct selling benefits consumers by providing convenience and service, such as personal demonstrations and explanations of goods, home delivery, and substantial satisfaction guarantees.
Discount club:
The discount club concept is built on perpetual high-discount deals utilized as a continual marketing plan or a brief period (usually one day). This might be seen as a reduction in the face value of an invoice prepared in advance of its payments in the medium or long term.
Experience selling:
An experience in the sales model describes how a typical user perceives or comprehends a system's operation. A product or service's value is enhanced when an extra customer experience is included. Visual representations of experience models are abstract diagrams or metaphors derived from recognizable objects, actions, or systems. User interfaces use a range of experience models to help users rapidly comprehend what is occurring in the design, where they are, and what they may do next. For example, a software experience model may depict the connection between two applications and the relationship between an application and different navigation methods and other system or software components.
Fast fashion:
Fast fashion is a phrase fashion retailers use to describe how designs travel rapidly from the catwalk to catch current fashion trends. The emphasis is on optimizing specific supply chain components to enable these trends to be developed and produced quickly and affordably, allowing the mainstream customer to purchase current apparel designs at a reduced price.
Franchising:
A franchise is a license that a business (franchisee) obtains to get access to a business's secret knowledge, procedures, and trademarks to promote a product or provide services under the company's business name. The franchisee typically pays the franchisee an initial startup cost and yearly licensing fees in return for obtaining the franchise.
From push to pull:
In business, a push-pull system refers to the flow of a product or information between two parties. Customers pull the products or information they need on markets, while offerers or suppliers push them toward them. In logistics and supply chains, stages often operate in both push and pull modes. For example, push production is forecasted demand, while pull production is actual or consumer demand. The push-pull border or decoupling point is the contact between these phases. Wal-Mart is a case of a company that employs a push vs. a pull approach.
Ingredient branding:
Ingredient branding is a kind of marketing in which a component or ingredient of a product or service is elevated to prominence and given its own identity. It is the process of developing a brand for an element or component of a product in order to communicate the ingredient's superior quality or performance. For example, everybody is aware of the now-famous Intel Inside and its subsequent success.
Layer player:
Companies that add value across many markets and sectors are referred to be layer players. Occasionally, specialist companies achieve dominance in a specific niche market. The effectiveness of their operations, along with their economies of size and footprint, establish the business as a market leader.
Licensing:
A formal agreement in which the owner of the copyright, know-how, patent, service mark, trademark, or other intellectual property grants a licensee the right to use, manufacture, and sell copies of the original. These agreements often restrict the licensee's scope or area of operation, define whether the license is exclusive or non-exclusive, and stipulate whether the licensee will pay royalties or another kind of compensation in return. While licensing agreements are often used to commercialize the technology, franchisees also utilize them to encourage the sale of products and services.
Localized low cost:
In general, this business model is appropriate for standardized goods and services with minimal requirements and low consumer expectations that may be manufactured locally and branded worldwide. However, this company concept will succeed only if the following two criteria are satisfied. The first is contingent upon a sizable market presence in mature markets' urban regions. This circumstance enables businesses to capitalize on their established brand value in developing areas. The second criterion is that the product or service generates revenue or is self-sustaining. This circumstance creates the possibility of reduced earnings in developing economies.
Low cost:
A pricing strategy in which a business provides a low price in order to drive demand and increase market share. Additionally referred to as a low-price approach. The low-cost model has sparked a revolution in the airline industry. The end-user benefits from low-cost tickets as a result of a revenue strategy that seeks various sources of income. Ryanair was one of the first businesses to embrace this approach.
No frills:
A no frills service or product has been stripped of non-essential elements to keep the price low. Initially, the word frills referred to a kind of cloth embellishment. Something provided free of charge to clients may be a frill - for example, complimentary beverages on airline flights or a radio fitted in a rental vehicle. No-frills companies rely on the premise that by eliminating opulent extras, consumers may benefit from reduced costs. Budget airlines, supermarkets, holidays, and pre-owned cars are examples of everyday goods and services with no-frills branding.
Orchestrator:
Orchestrators are businesses that outsource a substantial portion of their operations and processes to third-party service providers or third-party vendors. The fundamental objective of this business strategy is to concentrate internal resources on core and essential functions while contracting out the remainder of the work to other businesses, thus reducing costs.
Self-service:
A retail business model in which consumers self-serve the goods they want to buy. Self-service business concepts include self-service food buffets, self-service petrol stations, and self-service markets. Self-service is available through phone, online, and email to automate customer support interactions. Self-service Software and self-service applications (for example, online banking apps, shopping portals, and self-service check-in at airports) are becoming more prevalent.
Shop in shop:
A store-within-a-store, sometimes known as a shop-in-shop, is an arrangement in which a retailer leases out a portion of its retail space to another business to operate another independent store. This arrangement is prevalent with gas stations and supermarkets. In addition, numerous bookstores collaborate with coffee shops since consumers often want a spot to relax and enjoy a beverage while browsing. Frequently, the shop-within-a-store is owned by a manufacturer who operates an outlet inside a retailer's store.
Sponsorship:
In most instances, support is not intended to be philanthropic; instead, it is a mutually beneficial commercial relationship. In the highly competitive sponsorship climate of sport, a business aligning its brand with a mark seeks a variety of economic, public relations, and product placement benefits. Sponsors also seek to establish public trust, acceptability, or alignment with the perceived image a sport has built or acquired by leveraging their connection with an athlete, team, league, or the sport itself.
Rent instead of buy:
Services that do not need the product to be purchased but rather rent it for the economic benefit of requiring less money to access the commodity. When you rent, you assume less obligation since most of the burden is placed on the owner's shoulders. There is no debt; you are just responsible for the monthly rent. When renting, you have more flexibility by signing a six-month or one-year lease. This implies that you will be confined to that location for at least that period. When your lease term expires, you have the option of switching to another product or renewing your lease.
Recommended companies based on your search: