Why Compass Group's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
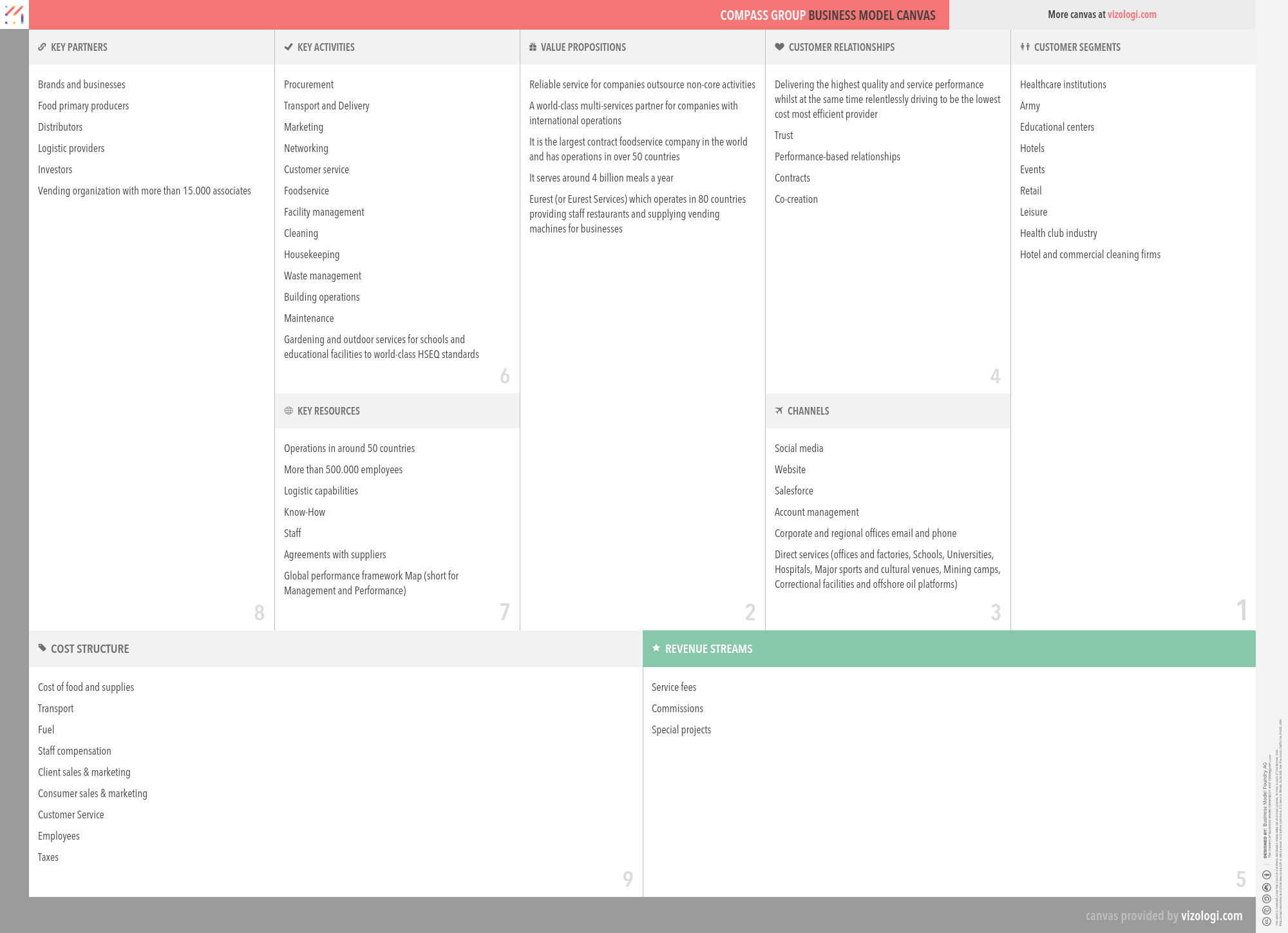
Compass Group’s Company Overview
Compass Group PLC provides food and support services. The company's Segments include North America, Europe, Rest of World and Central activities. The Europe Segment includes Turkey and Russia. The Rest of World Segment includes Japan. The company delivers services in sectors, including business and industry; healthcare and seniors; education; defense, offshore and remote, and sports and leisure. The company offers its services to customers in the workplace, schools and colleges, hospitals, at leisure and in remote environments. It provides breakfasts, lunches, and dinners, and also offers hospitality services. The company offers a range of support services, including cleaning, building operations and maintenance, business and office services, logistics and transport, outdoor, project management and security. Its foodservice offerings under healthcare and seniors sector include patient feeding, retail food courts, hospitality catering, vending, retail shops and staff restaurants.
www.compass-group.comCountry: London
Foundations date: 1941
Type: Public
Sector: Consumer Services
Categories: Food & Beverages
Compass Group’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing:
Emotional: wellness, badge value
Functional: saves time, organizes, reduces effort, quality, sensory appeal, integrates, variety
Compass Group’s Related Competitors
Compass Group’s Business Operations
Brands consortium:
A collection of brands that coexist under the auspices of a parent business. The businesses in this pattern develop, produce, and market equipment. Their strength is in copywriting. Occasionally used to refer to a short-term agreement in which many companies (from the same or other industrial sectors or countries) combine their financial and personnel resources to execute a significant project benefiting all group members.
Customer loyalty:
Customer loyalty is a very successful business strategy. It entails giving consumers value that extends beyond the product or service itself. It is often provided through incentive-based programs such as member discounts, coupons, birthday discounts, and points. Today, most businesses have some kind of incentive-based programs, such as American Airlines, which rewards customers with points for each trip they take with them.
Orchestrator:
Orchestrators are businesses that outsource a substantial portion of their operations and processes to third-party service providers or third-party vendors. The fundamental objective of this business strategy is to concentrate internal resources on core and essential functions while contracting out the remainder of the work to other businesses, thus reducing costs.
Performance-based contracting:
Performance-based contracting (PBC), sometimes referred to as performance-based logistics (PBL) or performance-based acquisition, is a method for achieving quantifiable supplier performance. A PBC strategy focuses on developing strategic performance measures and the direct correlation of contract payment to success against these criteria. Availability, dependability, maintainability, supportability, and total cost of ownership are all standard criteria. This is accomplished mainly via incentive-based, long-term contracts with precise and quantifiable operational performance targets set by the client and agreed upon by contractual parties.
Reseller:
Resellers are businesses or individuals (merchants) that acquire products or services to resell them instead of consuming or utilizing them. This is often done for financial gain (but could be resold at a loss). Resellers are well-known for doing business on the internet through websites. One instance is the telecommunications sector, in which corporations purchase surplus transmission capacity or take the call from other providers and resell it to regional carriers.
Solution provider:
A solution provider consolidates all goods and services in a particular domain into a single point of contact. As a result, the client is supplied with a unique know-how to improve efficiency and performance. As a Solution Provider, a business may avoid revenue loss by broadening the scope of the service it offers, which adds value to the product. Additionally, close client interaction enables a better understanding of the customer's habits and requirements, enhancing goods and services.
Supply chain:
A supply chain is a network of companies, people, activities, data, and resources that facilitate the movement of goods and services from supplier to consumer. The supply chain processes natural resources, raw materials, and components into a completed product supplied to the ultimate consumer. In addition, used goods may re-enter the distribution network at any point where residual value is recyclable in advanced supply chain systems. Thus, value chains are connected through supply chains.
Recommended companies based on your search: