Why Patreon's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
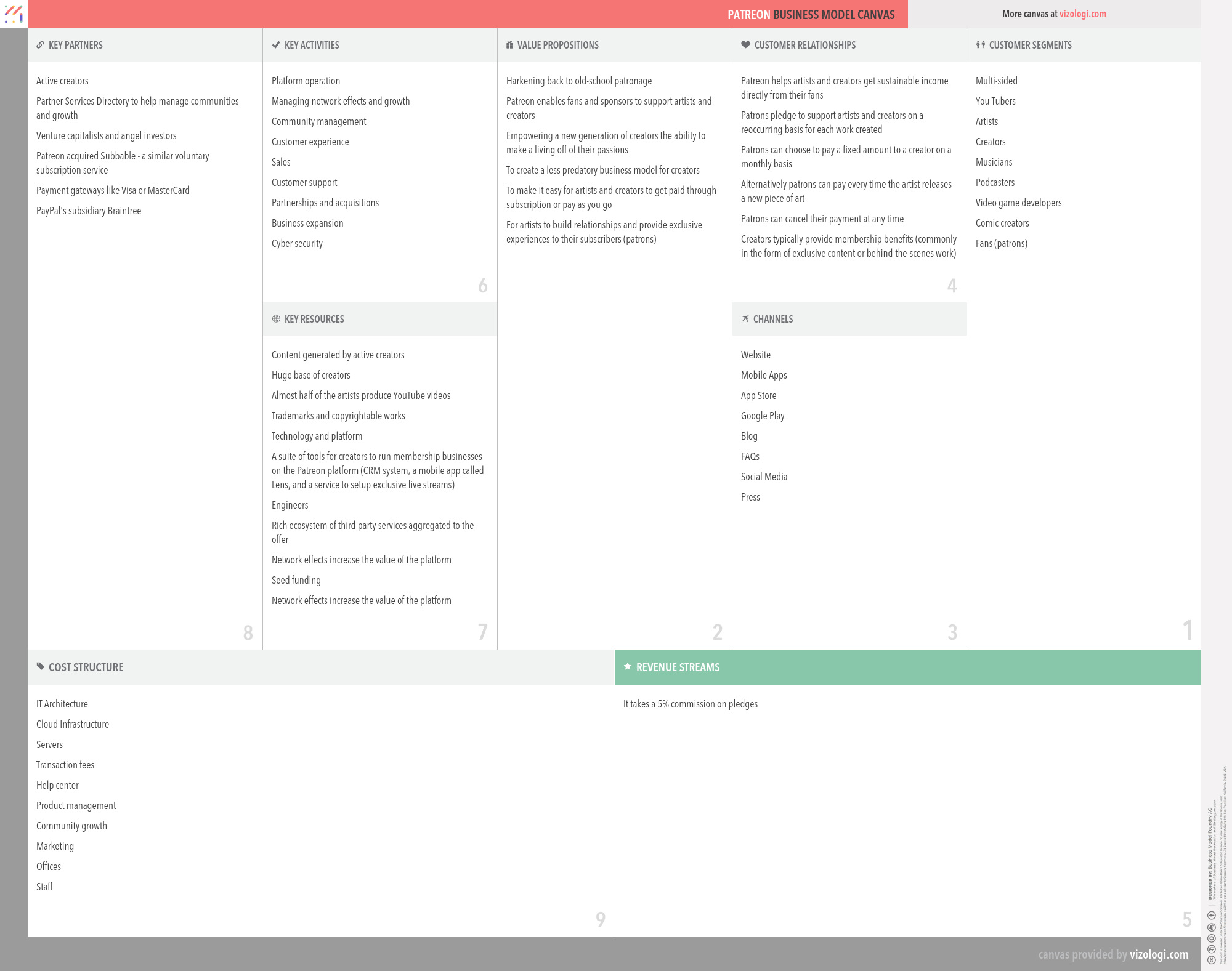
Patreon’s Company Overview
Patreon is an internet-based platform that allows content creators to build their own subscription content service. It is popular among YouTube content creators, webcomic artists, writers, podcasters, musicians, and other categories of creators who post regularly online. It allows artists to receive funding directly from their fans, or patrons, on a recurring basis or per work of art. The company, started by musician Jack Conte and developer Sam Yam in 2013, is based in San Francisco
https://www.patreon.comCountry: California
Foundations date: 2013
Type: Private
Sector: Information & Media
Categories: Entertainment
Patreon’s Customer Needs
Social impact: self-transcendence
Life changing: self-actualization
Emotional: badge value, provides access, rewards me, fun/entertainment, design/aesthetics
Functional: makes money, organizes, connects, variety, informs, integrates, sensory appeal
Patreon’s Related Competitors
Patreon’s Business Operations
Access over ownership:
The accessibility over ownership model is a business concept that allows consumers to utilize a product without owning it. Everything serves a purpose. As a result, consumers all across the Western world are demanding more value from their goods and services, and they are rethinking their relationship with stuff.' Furthermore, with thriving online communities embracing the idea of access above ownership, the internet is developing as a robust platform for sharing models to expand and prosper.
Add-on:
An additional item offered to a customer of a primary product or service is referred to as an add-on sale. Depending on the industry, add-on sales may generate substantial income and profits for a firm. For example, when a customer has decided to purchase the core product or service, the salesman at an automotive dealership will usually offer an add-on sale. The pattern is used in the price of new software programs based on access to new features, number of users, and so forth.
Aikido:
The aikido business model is often characterized as using a competitor's strength to get an edge over them. This is accomplished through finding weaknesses in a competitor's strategic position. In addition, it adds to marketing sustainability by exposing rivals' flaws, finding internal and external areas for development, and attracting consumers via specific product offers that deviate from the norm.
Brokerage:
A brokerage firm's primary responsibility is to serve as a middleman, connecting buyers and sellers to complete transactions. Accordingly, brokerage firms are compensated through commission once a transaction is completed. For example, when a stock trade order is executed, a transaction fee is paid by an investor to repay the brokerage firm for its efforts in completing the transaction.
Community-funded:
The critical resource in this business strategy is a community's intellect. Three distinct consumer groups comprise this multifaceted business model: believers, suppliers, and purchasers. First, believers join the online community platform and contribute to the production of goods by vendors. Second, buyers purchase these goods, which may be visual, aural, or literary in nature. Finally, believers may be purchasers or providers, and vice versa.
Crowdfunding:
Crowdfunding is the technique by which a large number of people contribute to a project. Contribute modest sums of money to support a new business endeavor. Crowdfunding leverages the ease of accessing vast networks of people, connecting investors and entrepreneurs through social media and crowdfunding websites. It can increase entrepreneurialism by widening the pool of investors further than the traditional ring of owners, relatives, and venture capitalists.
Crowdsourcing:
Crowdsourcing is a kind of sourcing in which people or organizations solicit donations from Internet users to acquire required services or ideas. Crowdsourcing differs from outsourcing because work may originate from an undefined public (rather than being commissioned from a particular, identified organization). In addition, those crowdsourcing procedures are a combination of bottom-up and top-down. The benefits of crowdsourcing may include reduced prices, increased speed, better quality, increased flexibility, scalability, and variety. An anonymous crowd adopts a solution to a task or issue, usually through the internet. Contributors are compensated or have the opportunity to win a prize if their answer is selected for manufacturing or sale. Customer engagement and inclusion may help build a good rapport with them, resulting in increased sales and income.
Disintermediation:
Keeping the purchase price low by avoiding mediators and maximizing supply margins is a win-win situation. In finance, disintermediation refers to how money is removed from intermediate financial organizations such as banks and savings and loan associations and invested directly. Disintermediation, in general, refers to the process of eliminating the middleman or intermediary from future transactions. Disintermediation is often used to invest in higher-yielding securities.
Disruptive trends:
A disruptive technology supplants an existing technology and fundamentally alters an industry or a game-changing innovation that establishes an altogether new industry. Disruptive innovation is defined as an invention that shows a new market and value network and ultimately disrupts an established market and value network, replacing incumbent market-leading companies, products, and alliances.
Donation-based:
Crowdfunding for charity purposes is a collaborative effort by people to aid charitable projects. Civic crowdfunding is a kind of charity crowdfunding in which money is collected to improve public life and space.
Dynamic pricing:
This pattern allows the business to adjust its rates in response to national or regional trends. Dynamic pricing is a pricing technique known as surge pricing, demand pricing, or time-based pricing. In which companies establish variable prices for their goods or services in response to changing market conditions. Companies may adjust their rates based on algorithms that consider rival pricing, supply and demand, and other market variables. Dynamic pricing is widely used in various sectors, including hospitality, travel, entertainment, retail, energy, and public transportation.
Low-budget innovation:
Fast-moving consumer goods businesses produce co-created items with early adopters through sample testing based on user observation and involvement. As a result, fast-moving consumer goods businesses may obtain a greater new product success rate while incurring fewer development expenses via a low-budget innovation business strategy. That is referred to as low-budget innovation.
Network builders:
This pattern is used to connecting individuals. It offers essential services for free but charges for extra services. The network effect is a paradox that occurs when more people utilize a product or service, the more valuable it becomes.
Online marketplace:
An online marketplace (or online e-commerce marketplace) is a kind of e-commerce website in which product or service information is supplied by various third parties or, in some instances, the brand itself, while the marketplace operator handles transactions. Additionally, this pattern encompasses peer-to-peer (P2P) e-commerce between businesses or people. By and large, since marketplaces aggregate goods from a diverse range of suppliers, the variety and availability are typically greater than in vendor-specific online retail shops. Additionally, pricing might be more competitive.
Reputation builders:
Reputation builders is an innovative software platform that enables companies to create, collect, and manage positive internet reviews. It was a pioneer in the utilization of user-generated material. The website services are provided for free to users, who supply the majority of the content, and the websites of related businesses are monetized via advertising.
Two-sided market:
Two-sided marketplaces, also called two-sided networks, are commercial platforms featuring two different user groups that mutually profit from the web. A multi-sided platform is an organization that generates value mainly via the facilitation of direct contacts between two (or more) distinct kinds of connected consumers (MSP). A two-sided market enables interactions between many interdependent consumer groups. The platform's value grows as more groups or individual members of each group use it. For example, eBay is a marketplace that links buyers and sellers. Google connects advertising and searchers. Social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook are also bidirectional, linking consumers and marketers.
Unlimited niches:
Online retailers provide specialized content to various niche client groups via continuing mass-customized customer relationships. The sector of technical content providers is a second client segment. Combining these two factors may result in an infinite number of niches. New material is produced and distributed through online channels, which implies that online retailers must prioritize platform maintenance and marketing in addition to service delivery.
Recommended companies based on your search: