Why Tupperware's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
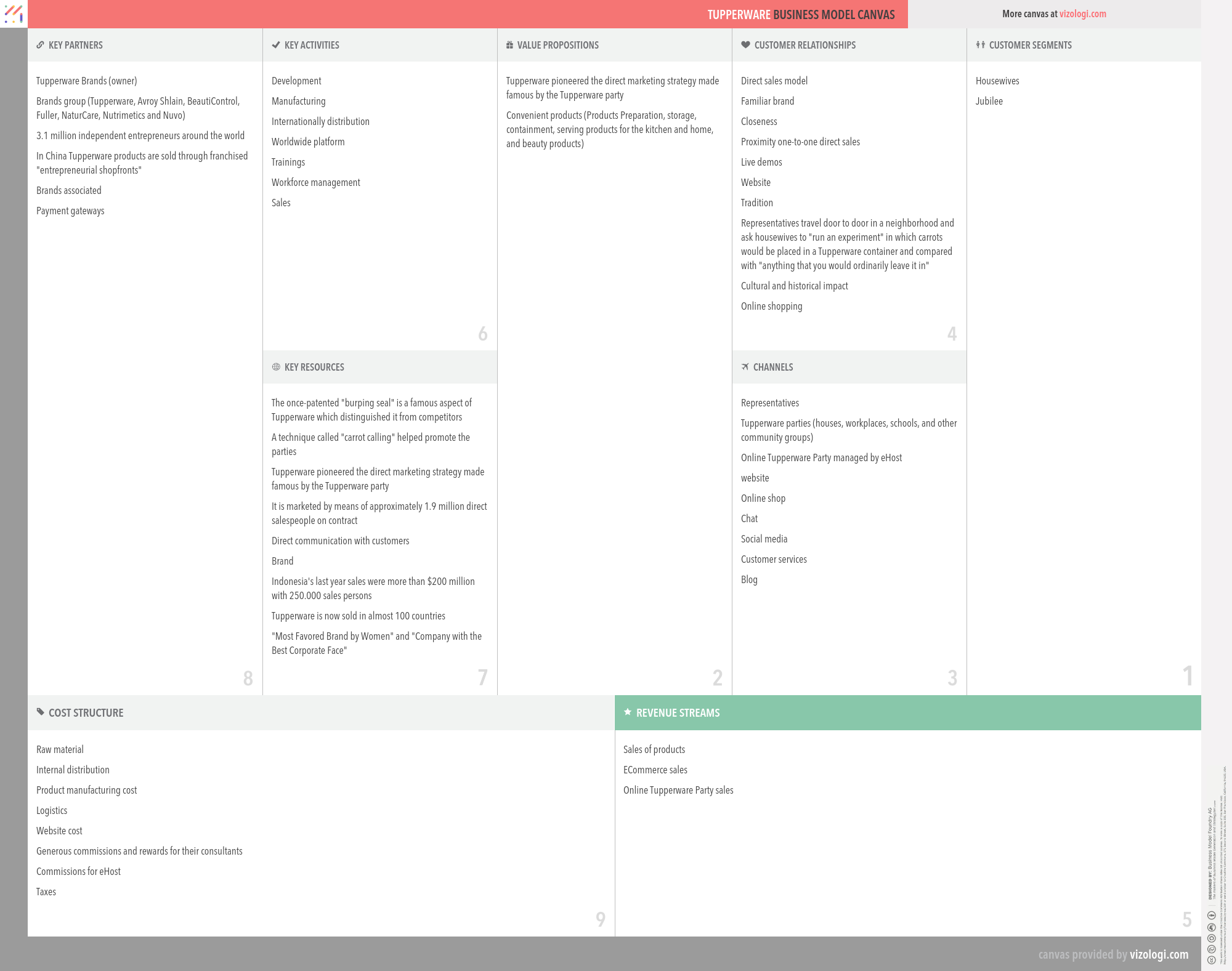
Tupperware’s Company Overview
Tupperware Brands Corporation, formerly Tupperware Corporation, is an American multinational direct sales company. The company was ranked equal # 2 in Fortune's Most Admired Home equipment and furnishings section.
www.tupperware.comCountry: Florida
Foundations date: 1948
Type: Subsidiary
Sector: Consumer Goods
Categories: Retail
Tupperware’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: affiliation/belonging
Emotional: nostalgia, badge value
Functional: variety, sensory appeal
Tupperware’s Related Competitors
Tupperware’s Business Operations
Direct selling:
Direct selling refers to a situation in which a company's goods are immediately accessible from the manufacturer or service provider rather than via intermediate channels. The business avoids the retail margin and any extra expenses connected with the intermediaries in this manner. These savings may be passed on to the client, establishing a consistent sales experience. Furthermore, such intimate touch may help to strengthen client connections. Finally, direct selling benefits consumers by providing convenience and service, such as personal demonstrations and explanations of goods, home delivery, and substantial satisfaction guarantees.
Ingredient branding:
Ingredient branding is a kind of marketing in which a component or ingredient of a product or service is elevated to prominence and given its own identity. It is the process of developing a brand for an element or component of a product in order to communicate the ingredient's superior quality or performance. For example, everybody is aware of the now-famous Intel Inside and its subsequent success.
Franchising:
A franchise is a license that a business (franchisee) obtains to get access to a business's secret knowledge, procedures, and trademarks to promote a product or provide services under the company's business name. The franchisee typically pays the franchisee an initial startup cost and yearly licensing fees in return for obtaining the franchise.
Experience selling:
An experience in the sales model describes how a typical user perceives or comprehends a system's operation. A product or service's value is enhanced when an extra customer experience is included. Visual representations of experience models are abstract diagrams or metaphors derived from recognizable objects, actions, or systems. User interfaces use a range of experience models to help users rapidly comprehend what is occurring in the design, where they are, and what they may do next. For example, a software experience model may depict the connection between two applications and the relationship between an application and different navigation methods and other system or software components.
Long tail:
The long tail is a strategy that allows businesses to realize significant profit out of selling low volumes of hard-to-find items to many customers instead of only selling large volumes of a reduced number of popular items. The term was coined in 2004 by Chris Anderson, who argued that products in low demand or with low sales volume can collectively make up market share that rivals or exceeds the relatively few current bestsellers and blockbusters but only if the store or distribution channel is large enough.
Multi-level marketing:
MLM, also known as pyramid selling, network marketing, and referral marketing, is a type of multi-level marketing, is a contentious pyramid-shaped marketing technique that generates profit from two income sources. From a participating salesperson's sales force, which is paid based on the salesperson's direct sales as well as the sales of other salespeople whom the participating salesperson recruited and their recruiters down the line.
Revenue sharing:
Revenue sharing occurs in various forms, but each iteration includes the sharing of operational gains or losses amongst connected financial players. Occasionally, revenue sharing is utilized as an incentive program ? for example, a small company owner may pay partners or colleagues a percentage-based commission for recommending new clients. Occasionally, revenue sharing is utilized to share the earnings generated by a corporate partnership.
Online marketplace:
An online marketplace (or online e-commerce marketplace) is a kind of e-commerce website in which product or service information is supplied by various third parties or, in some instances, the brand itself, while the marketplace operator handles transactions. Additionally, this pattern encompasses peer-to-peer (P2P) e-commerce between businesses or people. By and large, since marketplaces aggregate goods from a diverse range of suppliers, the variety and availability are typically greater than in vendor-specific online retail shops. Additionally, pricing might be more competitive.
Experience:
Disrupts by offering a better understanding that customers are willing to pay for. Experience companies that have progressed may begin charging for the value of the transformation that an experience provides. An experienced company charges for the feelings consumers get as a result of their interaction with it.
eCommerce:
Electronic commerce, or e-commerce (alternatively spelled eCommerce), is a business model, or a subset of a larger business model, that allows a company or person to do business via an electronic network, usually the internet. As a result, customers gain from increased accessibility and convenience, while the business benefits from integrating sales and distribution with other internal operations. Electronic commerce is prevalent throughout all four main market segments: business to business, business to consumer, consumer to consumer, and consumer to business. Ecommerce may be used to sell almost any goods or service, from books and music to financial services and airline tickets.
Niche retail:
A marketing strategy for a product or service includes characteristics that appeal to a particular minority market segment. A typical niche product will be distinguishable from other goods and manufactured and sold for specialized purposes within its associated niche market. Niche retail has focused on direct-to-consumer and direct-to-business internet sales channels. The slogan for niche retail is Everything except the brand.
Low touch:
Historically, developing a standard touch sales model for business sales required recruiting and training a Salesforce user who was tasked with the responsibility of generating quality leads, arranging face-to-face meetings, giving presentations, and eventually closing transactions. However, the idea of a low-touch sales strategy is not new; it dates all the way back to the 1980s.
Recommended companies based on your search: