Why UPS's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
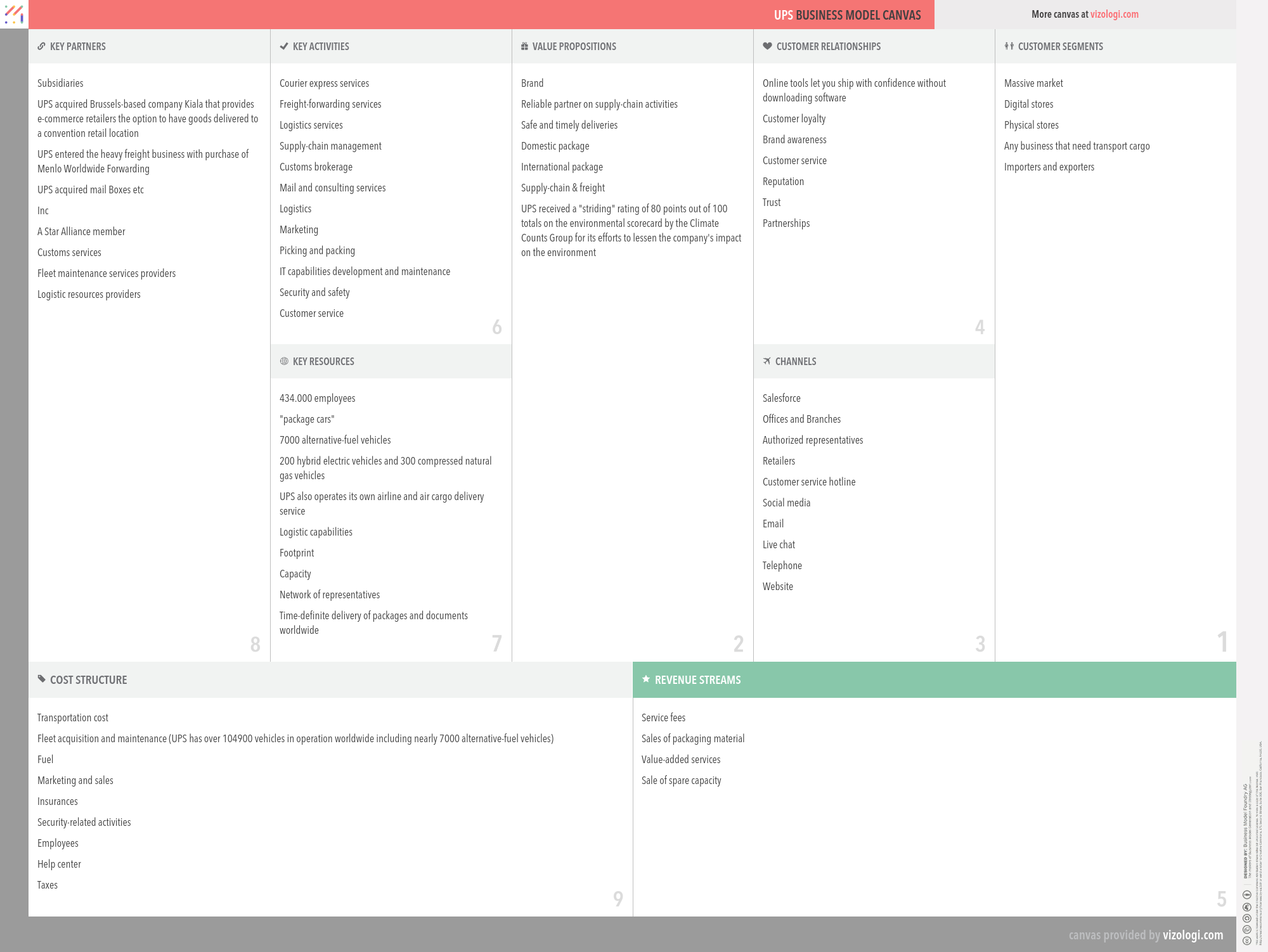
UPS’s Company Overview
United Parcel Service, Inc. (UPS) is the world's largest package delivery company and a provider of supply-chain management solutions. UPS delivers more than 15 million packages per day to more than 7.9 million customers in more than 220 countries and territories around the world. UPS is known for its brown delivery trucks and uniforms, hence the company nickname "Brown."
www.ups.comCountry: Georgia
Foundations date: 1907
Type: Public
Sector: Transportation
Categories: Logistics
UPS’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing:
Emotional: provides access, badge value, rewards me
Functional: connects, avoid hassles, reduces risks, saves time, reduces effort, organizes, integrates, simplifies, quality, informs
UPS’s Related Competitors
UPS’s Business Operations
Add-on:
An additional item offered to a customer of a primary product or service is referred to as an add-on sale. Depending on the industry, add-on sales may generate substantial income and profits for a firm. For example, when a customer has decided to purchase the core product or service, the salesman at an automotive dealership will usually offer an add-on sale. The pattern is used in the price of new software programs based on access to new features, number of users, and so forth.
Best in class services:
When a firm brings a product to market, it must first create a compelling product and then field a workforce capable of manufacturing it at a competitive price. Neither task is simple to perform effectively; much managerial effort and scholarly study have been dedicated to these issues. Nevertheless, providing a service involves another aspect: managing clients, who are consumers of the service and may also contribute to its creation.
Bundling:
Multiple products or services have been bundled together to enhance the value. Bundling is a marketing technique in which goods or services are bundled to be sold as a single entity. Bundling enables the purchasing of several goods and services from a single vendor. While the goods and services are often linked, they may also consist of different items that appeal to a particular market segment.
Cash machine:
The cash machine business model allows companies to obtain money from sales since consumers pay ahead for the goods they purchase, but the costs required to generate the revenue are not yet paid. This increases companies' liquidity, which they may use to pay off debt or make additional investments. Among several others, the online store Amazon often employs this business model.
Customer loyalty:
Customer loyalty is a very successful business strategy. It entails giving consumers value that extends beyond the product or service itself. It is often provided through incentive-based programs such as member discounts, coupons, birthday discounts, and points. Today, most businesses have some kind of incentive-based programs, such as American Airlines, which rewards customers with points for each trip they take with them.
Digital:
A digital strategy is a strategic management and a business reaction or solution to a digital issue, which is often best handled as part of a broader company plan. A digital strategy is frequently defined by the application of new technologies to existing business activities and a focus on enabling new digital skills for their company (such as those formed by the Information Age and frequently as a result of advances in digital technologies such as computers, data, telecommunication services, and the World wide web, to name a few).
Integrator:
A systems integrator is an individual or business specializing in integrating component subsystems into a unified whole and ensuring that those subsystems work correctly together. A process is known as system integration. Gains in efficiency, economies of scope, and less reliance on suppliers result in cost reductions and may improve the stability of value generation.
Layer player:
Companies that add value across many markets and sectors are referred to be layer players. Occasionally, specialist companies achieve dominance in a specific niche market. The effectiveness of their operations, along with their economies of size and footprint, establish the business as a market leader.
Make more of It:
The business invests time and money in developing in-house expertise and development that may be used both internally and outside to sell goods or services to clients or third parties. AWS was created to meet Amazon's cloud computing requirements. They quickly discovered that they could offer their services to end-users. At the moment, AWS accounts for about 11% of Amazon's overall income.
Pay as you go:
Pay as you go (PAYG) business models charge based on actual consumption or use of a product or service. Specific mobile phone contracts work on this principle, in which the user may purchase a phone card that provides credit. However, each call is billed separately, and the credit balance is depleted as the minutes are used (in contrast to subscription models where you pay a monthly fee for calls). Pay as you go is another term for pay & go, pay per use, pay per use, or pay-as-you-go.
Performance-based contracting:
Performance-based contracting (PBC), sometimes referred to as performance-based logistics (PBL) or performance-based acquisition, is a method for achieving quantifiable supplier performance. A PBC strategy focuses on developing strategic performance measures and the direct correlation of contract payment to success against these criteria. Availability, dependability, maintainability, supportability, and total cost of ownership are all standard criteria. This is accomplished mainly via incentive-based, long-term contracts with precise and quantifiable operational performance targets set by the client and agreed upon by contractual parties.
Solution provider:
A solution provider consolidates all goods and services in a particular domain into a single point of contact. As a result, the client is supplied with a unique know-how to improve efficiency and performance. As a Solution Provider, a business may avoid revenue loss by broadening the scope of the service it offers, which adds value to the product. Additionally, close client interaction enables a better understanding of the customer's habits and requirements, enhancing goods and services.
Supply chain:
A supply chain is a network of companies, people, activities, data, and resources that facilitate the movement of goods and services from supplier to consumer. The supply chain processes natural resources, raw materials, and components into a completed product supplied to the ultimate consumer. In addition, used goods may re-enter the distribution network at any point where residual value is recyclable in advanced supply chain systems. Thus, value chains are connected through supply chains.
Sustainability-focused:
Companies that manufacture fast-moving consumer goods and services and are committed to sustainability do ecological impact assessments on their products and services. While research-based green marketing needs facts, green storytelling requires imagination and location. Employees responsible for the brand definition and green marketers collaborate with product and service designers, environmental groups, and government agencies.
Recommended companies based on your search: