Problem-Solving in Business Analysis: Key Skills
Problem-solving is an important skill in business analysis. It helps professionals identify and address issues within an organization. From analyzing data to developing strategies, problem-solving is crucial for success.
In this article, we’ll explore the key skills needed for effective problem-solving in business analysis and discuss how developing these skills can help professionals make valuable contributions to their organizations.
The Essential Role of Problem-Solving for Business Analysts
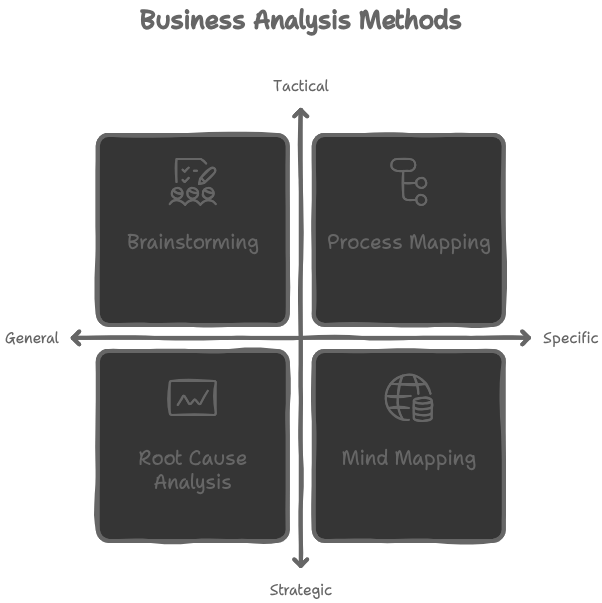
Business analysts play a crucial role in solving problems for businesses. They identify and analyze challenging issues to provide effective solutions. Methods like brainstorming, process mapping, and SWOT analysis help them address complex challenges. These techniques enable analysts to define problems, generate solutions, and identify the best one. They work collaboratively with stakeholders to ensure valuable solutions meet client needs.
Continuous improvement of problem-solving skills is important for effectively navigating work challenges.
Demonstrating Problem-Solving in Action: Business Analysis Scenarios
The business analyst uses brainstorming, process mapping, and root cause analysis to solve complex business challenges. They collaborate with stakeholders and subject matter experts to identify potential issues and conduct in-depth analyses.
For example, during a recent project, the business analyst facilitated a brainstorming session with the project team to generate innovative solutions for a critical business problem. This resulted in the development of an effective action plan to address the identified issues.
Like mind mapping concepts, strategic visualization is used to organize and prioritize various ideas and concepts visually, providing a clear and structured approach to identifying potential solutions.
Additionally, using structural tools and frameworks, such as the fishbone diagram, SWOT analysis, and Pareto chart, has helped the business analyst systematically analyze data, identify key areas for improvement, and prioritize actions based on the impact.
For instance, the business analyst used the SWOT analysis to assess the company’s competitive position. This enabled the identification of specific strategies to capitalize on strengths and opportunities while addressing weaknesses and threats.
Key Techniques to Address Complex Business Challenges
Business analysts use investigative methods to uncover core issues in complex business challenges. They apply structured problem-solving techniques and various tools, such as root cause analysis, the Five Whys technique, SWOT analysis, and the Pareto chart, to resolve problems. These tools help identify and analyze the root causes of problems and make informed decisions based on data.
Brainstorming and process mapping can also be employed to generate innovative ideas and visually represent a process’s steps and key elements. By approaching problems with a structured, analytical mindset and collaborating with stakeholders, business analysts can effectively enhance their problem-solving skills and provide valuable solutions to clients.
Investigative Methods: Uncovering the Core Issues
Brainstorming Ideas
One way to generate and brainstorm new ideas for complex business challenges is to use techniques like mind mapping, the Five Whys, and root cause analysis. These methods help business analysts visualize concepts, identify patterns, and devise innovative solutions.
Mind mapping helps analysts visually organize ideas and concepts, leading to a better understanding of complex issues and potential solutions. The Five Whys and Root Cause Analysis Techniques allow analysts to explore the underlying causes of a problem and develop creative strategies to address it by asking sequential “why” questions. Then, analysts can uncover the root cause and brainstorm solutions.
These methods help develop problem-solving skills in business analysis by providing structured tools to collaboratively address complex business challenges effectively.
Process Mapping for Clarity
Process mapping is a helpful tool for business analysis. It visually represents a series of events and actions within a process, helping analysts find inefficiencies, redundancies, or bottlenecks that affect operational performance.
By using process mapping, analysts can emphasize the importance of clearly visualizing the operational process. This helps stakeholders understand the process better. It also allows analysts to uncover core issues and address complex business challenges by identifying areas for improvement and innovation.
Additionally, process mapping aids in strategic visualization and problem resolution. It creates a framework for analysts to examine the flow of work, inputs, and outputs, enhancing decision-making and problem-resolution within the organization.
Digging Deeper: Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a valuable tool for business analysts. It helps uncover the core issues in complex business challenges. By using techniques like the fishbone diagram or the Five Whys technique, they can find the underlying causes of a problem rather than just its symptoms.
For example, if a retail company’s sales decrease, a root cause analysis may reveal that it’s due to a shift in consumer preferences or increased competition rather than just ineffective marketing strategies.
The Five Whys technique empowers business analysts to go beyond surface-level symptoms by repeatedly asking “why” to get to the root cause. These techniques help them dig deeper and find long-term solutions to complex business problems.
To conduct a practical root cause analysis, business analysts must use various techniques such as brainstorming, process mapping, and SWOT analysis. Each technique provides a unique perspective and helps uncover the underlying issues. These structured approaches ensure that the root cause is accurately identified, allowing for the development of targeted and effective solutions.
For example, by using SWOT analysis, business analysts can assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with a problem, guiding their analysis to uncover the root cause.
Incisive Inquiry: The Five Whys Technique
The Five Whys Technique helps uncover the root cause of a problem in business analysis. It involves repeatedly asking “why” to reveal the trustworthy source of the issue. This approach is essential for addressing complex business challenges, allowing analysts to dig deep and identify the fundamental cause. The technique contributes to problem resolution and decision-making by providing a systematic approach to problem-solving.
It enables analysts to develop effective solutions that target the root cause instead of just treating the symptoms. For instance, if a business deals with recurring customer complaints about a product defect, the Five Whys Technique can pinpoint the specific flaws in the production process that need addressing for a permanent resolution.
Strategic Visualization: Mind Mapping Concepts
Strategic visualization through mind mapping is a helpful tool for problem-solving in business analysis. It organizes information visually, allowing analysts to see how different aspects of a problem relate.
Using this technique, analysts can map out key factors, stakeholders, and potential solutions in a structured way. This encourages creativity and flexibility when approaching challenges.
Mind mapping methods like brainstorming, process mapping, and SWOT analysis can be incorporated to address complex business challenges. These approaches offer a systematic way of exploring and evaluating solutions, fostering collaboration with stakeholders and an analytical mindset.
Strategic visualization through mind mapping helps uncover core issues by focusing on critical factors and relationships. It aids in identifying patterns and potential causes, leading to a deeper understanding of the problems at hand and more informed decision-making.
Structural Tools and Frameworks for Problem Resolution
Using Fishbone Diagrams for Cause and Effect
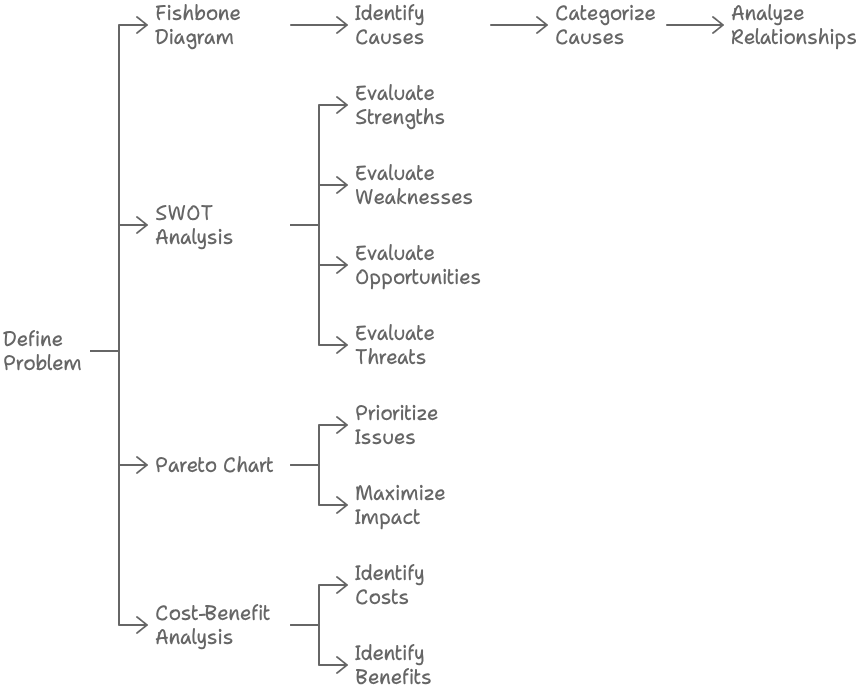
The Fishbone Diagram is a helpful tool for business analysts. It helps identify the causes and effects of a business problem. Analysts use this technique to visualize the different factors contributing to an issue, which can help them understand the root causes.
The key steps involved in using the Fishbone Diagram include:
- Defining the problem.
- Brainstorming potential causes.
- Categorizing causes into major groups.
- Analyzing the relationships between them
This process helps to organize and prioritize the key factors affecting the problem.
Moreover, the Fishbone Diagram aids in visualizing and understanding complex business challenges. It provides a structured approach to problem-solving, enabling stakeholders to identify the interdependencies between various contributing factors.
This visual representation facilitates a better understanding of the problem. It leads to practical solutions and informed decision-making.
Assessing Scenarios with SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is a helpful tool for evaluating business scenarios. It identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the current business situation. By examining these aspects, analysts can better understand how different factors might impact the business. They might find internal strengths to exploit external opportunities or spot weaknesses to address potential threats.
This analysis informs strategic plans and helps with making informed business decisions.
Pareto Chart: Prioritizing Issues for Maximum Impact
The Pareto Chart is a powerful tool for business analysts. It helps prioritize issues for maximum impact. By focusing on the most significant problems, analysts can allocate resources and make strategic decisions. When using a Pareto Chart, gathering and analyzing relevant data is essential. This helps identify common or severe issues affecting the business. The chart visually represents the frequency and impact of the various problems.
This aids analysts in making informed decisions about which issue to address first.
As a result, resources can be allocated more effectively, and solutions can deliver maximum value to the business and its stakeholders.
Quantitative Decisions: Cost-Benefit Analysis Process
Quantitative analysis helps businesses make cost-benefit decisions. It compares the costs and benefits of a decision to determine whether it is feasible and profitable.
For example, a manufacturing company might use it to decide if new machinery will save money and increase productivity over time. Key steps include identifying all costs and benefits, adjusting for the time value of money, and ensuring all relevant factors are included. Businesses can make better decisions by considering both tangible and intangible factors, such as environmental impact and employee satisfaction. Applying this process to different scenarios helps choose a profitable market, find a cost-effective supplier, or evaluate the return on investment for a new product or service.
Decision Matrix: Evaluating and Prioritizing Business Options
Business analysts should consider several relevant factors when evaluating and prioritizing business options using a decision matrix. These include cost, risk, potential return on investment, timeline, and resource requirements.
This approach allows for a comprehensive assessment of each option’s pros and cons, enabling them to make well-informed decisions.
A decision matrix can effectively compare and contrast various business options by assigning weights to each factor and scoring each option accordingly.
By summing up the scores, analysts can identify the most viable option that aligns with the organization’s objectives.
Implementing a decision matrix involves several key steps. These include determining evaluation criteria, gathering stakeholder input, assigning weights to criteria, scoring each option, and calculating the final scores.
This meticulous process ensures a thorough evaluation and prioritization of business options, leading to strategic and successful decision-making.
Advanced Problem-Solving: Employing CATWOE as a Tool
CATWOE is a useful tool for business analysts. It helps analyze complex business problems thoroughly. Using CATWOE, analysts can consider the broader context of the problem and understand stakeholders’ perspectives. This includes Customers, Actors, the Transformation Process, the worldview, and the Owner/Employer. This ensures that all viewpoints are carefully examined.
For instance, if a business is facing a decline in customer satisfaction, CATWOE can help understand not only customer perspectives but also the impact on employees, the transformation process, and other relevant aspects. This helps address the root causes of issues rather than just symptoms.
CATWOE empowers business analysts to develop strategic and sustainable solutions for complex business challenges. This enhances their investigative and decision-making methods, leading to more effective problem-solving.

Vizologi is a revolutionary AI-generated business strategy tool that offers its users access to advanced features to create and refine start-up ideas quickly.
It generates limitless business ideas, gains insights on markets and competitors, and automates business plan creation.


