Why Kroger's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
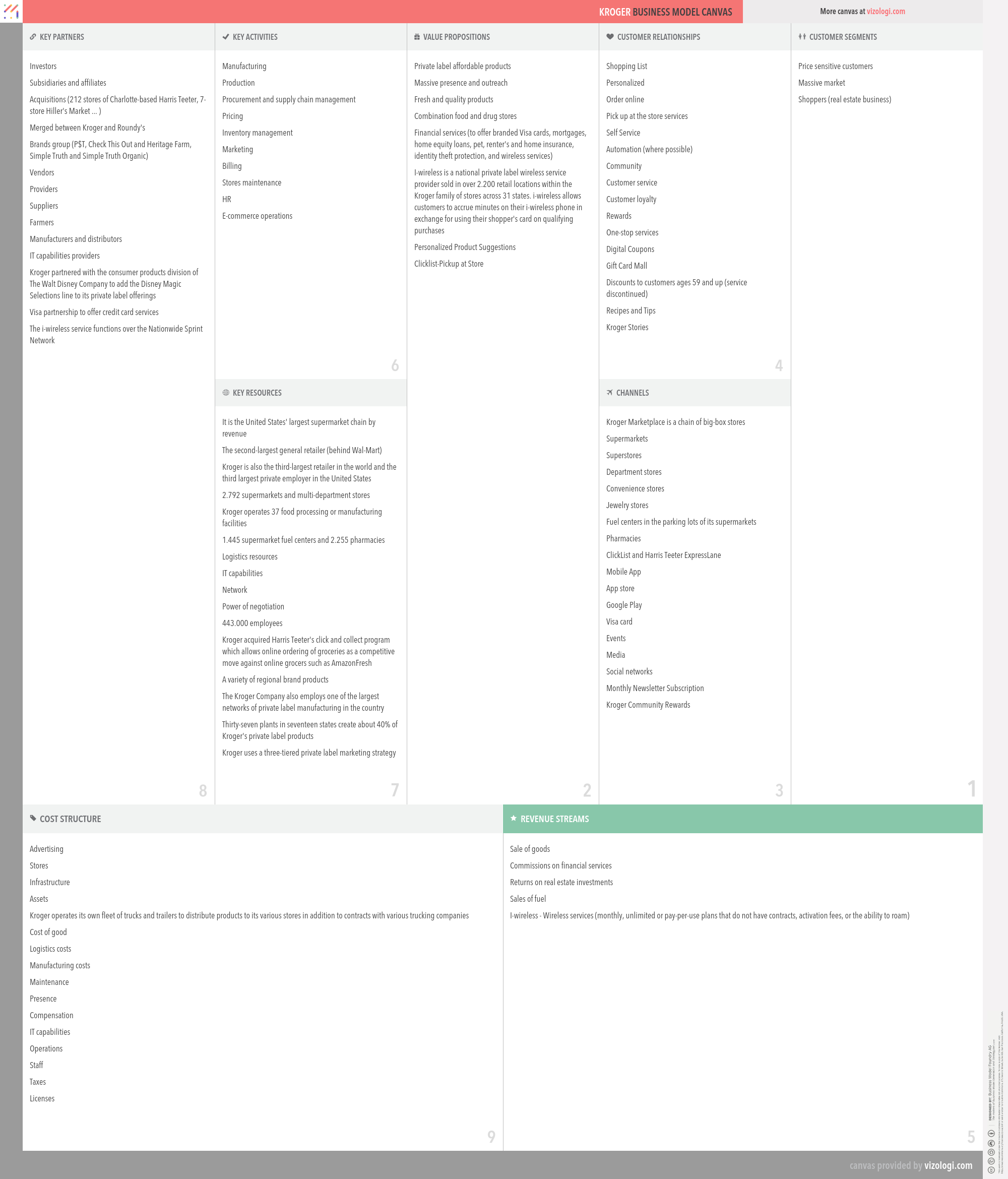
Kroger’s Company Overview
The Kroger Co. (Kroger) manufactures and processes food for sale in its supermarkets. The Company operates supermarkets, multi-department stores, jewelry stores and convenience stores throughout the United States. As of January 28, 2017, it had operated approximately 4.000 owned or leased supermarkets, convenience stores, fine jewelry stores, distribution warehouses and food production plants through divisions, subsidiaries or affiliates. These facilities are located throughout the United States. As of January 28, 2017, Kroger operated, either directly or through its subsidiaries, 2.796 supermarkets under a range of local banner names, of which 2,255 had pharmacies and 1,445 had fuel centers.
https://www.kroger.comCountry: Ohio
Foundations date: 1883
Type: Public
Sector: Consumer Goods
Categories: Retail
Kroger’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: affiliation/belonging
Emotional: provides access, rewards me, badge value, attractiveness
Functional: saves time, simplifies, reduces effort, quality, variety, sensory appeal, reduces cost
Kroger’s Related Competitors
Kroger’s Business Operations
Curated retail:
Curated retail guarantees focused shopping and product relevance; it presents a consumer with the most appropriate options based on past purchases, interactions, and established preferences. It may be provided via human guidance, algorithmic recommendations, or a combination of the two.
Channel aggregation:
Consolidating numerous distribution routes into one to achieve greater economic efficiency. A business model for internet commerce in which a company (that does not manufacture or warehouse any item) gathers (aggregates) information about products and services from many competing sources and displays it on its website. The firm's strength is in its power to create an 'environment' that attracts users to its website and develop a system that facilitates pricing and specification matching.
Cross-selling:
Cross-selling is a business strategy in which additional services or goods are offered to the primary offering to attract new consumers and retain existing ones. Numerous businesses are increasingly diversifying their product lines with items that have little resemblance to their primary offerings. Walmart is one such example; they used to offer everything but food. They want their stores to function as one-stop shops. Thus, companies mitigate their reliance on particular items and increase overall sustainability by providing other goods and services.
Brokerage:
A brokerage firm's primary responsibility is to serve as a middleman, connecting buyers and sellers to complete transactions. Accordingly, brokerage firms are compensated through commission once a transaction is completed. For example, when a stock trade order is executed, a transaction fee is paid by an investor to repay the brokerage firm for its efforts in completing the transaction.
Credits:
A credit arrangement is when a consumer purchases items on credit (without paying cash) and spends the provider later. Typically, trade credit is extended for a certain number of days after the products are delivered. These credits may be deducted from one's tax liability.
Advertising:
This approach generated money by sending promotional marketing messages from other businesses to customers. When you establish a for-profit company, one of the most critical aspects of your strategy is determining how to generate income. Many companies sell either products or services or a mix of the two. However, advertisers are frequently the source of the majority of all of the revenue for online businesses and media organizations. This is referred to as an ad-based income model.
Barter:
Without currency, it is a kind of trading in which products or services are traded. Typically used during periods of high inflation or scarcity of money, barter has become a popular method of negotiating agreements such as offers to purchase excess products in return for advertising space or time. With the introduction of the internet, bartering shifted from a largely person-to-person transaction to a primarily business-to-business one, where every day, commodities ranging from manufacturing capacity to steel and paper are bartered across international boundaries.
Archetypes of business model design:
The business model archetypes include many business personalities and more than one business model linked to various goods or services. There is a common foundation behind the scenes of each unit, but from a management standpoint, each group may operate independently.
Affiliation:
Commissions are used in the affiliate revenue model example. Essentially, you resell goods from other merchants or businesses on your website or in your physical store. You are then compensated for referring new consumers to the company offering the goods or services. Affiliates often use a pay-per-sale or pay-per-display model. As a result, the business can access a more diversified prospective client base without extra active sales or marketing efforts. Affiliate marketing is a popular internet business strategy with significant potential for growth. When a client purchases via a referral link, the affiliate gets a portion of the transaction's cost.
Customer loyalty:
Customer loyalty is a very successful business strategy. It entails giving consumers value that extends beyond the product or service itself. It is often provided through incentive-based programs such as member discounts, coupons, birthday discounts, and points. Today, most businesses have some kind of incentive-based programs, such as American Airlines, which rewards customers with points for each trip they take with them.
Customer data:
It primarily offers free services to users, stores their personal information, and acts as a platform for users to interact with one another. Additional value is generated by gathering and processing consumer data in advantageous ways for internal use or transfer to interested third parties. Revenue is produced by either directly selling the data to outsiders or by leveraging it for internal reasons, such as increasing the efficacy of advertising. Thus, innovative, sustainable Big Data business models are as prevalent and desired as they are elusive (i.e., data is the new oil).
Channel per purpose:
Creating separate channels for selling and purchasing current goods and services. A marketing plan is a vendor's plan for distributing a product or service to the end consumer through the chain of commerce. Manufacturers and retailers have a plethora of channel choices. The simplest method is the direct channel, which involves the seller selling directly to the consumer. In addition, the vendor may use its own sales staff or offer its goods or services through an e-commerce website.
Decomposition:
Simplifying many product kinds inside a product group or set of goods. A technique for doing business analysis in which a complex business process is dissected to reveal its constituent parts. Functional decomposition is a technique that may be used to contribute to an understanding and management of large and complicated processes and assist in issue solving. Additionally, functional decomposition is utilized in computer engineering to aid in the creation of software.
Brands consortium:
A collection of brands that coexist under the auspices of a parent business. The businesses in this pattern develop, produce, and market equipment. Their strength is in copywriting. Occasionally used to refer to a short-term agreement in which many companies (from the same or other industrial sectors or countries) combine their financial and personnel resources to execute a significant project benefiting all group members.
Cross-subsidiary:
When products and goods and products and services are integrated, they form a subsidiary side and a money side, maximizing the overall revenue impact. A subsidiary is a firm owned entirely or in part by another business, referred to as the parent company or holding company. A parent company with subsidiaries is a kind of conglomerate, a corporation that consists of several distinct companies; sometimes, the national or worldwide dispersion of the offices necessitates the establishment of subsidiaries.
Digital transformation:
Digitalization is the systematic and accelerated transformation of company operations, processes, skills, and models to fully exploit the changes and possibilities brought about by digital technology and its effect on society. Digital transformation is a journey with many interconnected intermediate objectives, with the ultimate aim of continuous enhancement of processes, divisions, and the business ecosystem in a hyperconnected age. Therefore, establishing the appropriate bridges for the trip is critical to success.
Discount club:
The discount club concept is built on perpetual high-discount deals utilized as a continual marketing plan or a brief period (usually one day). This might be seen as a reduction in the face value of an invoice prepared in advance of its payments in the medium or long term.
Corporate innovation:
Innovation is the outcome of collaborative creativity in turning an idea into a feasible concept, accompanied by a collaborative effort to bring that concept to life as a product, service, or process improvement. The digital era has created an environment conducive to business model innovation since technology has transformed how businesses operate and provide services to consumers.
Codifying a distinctive service capability:
Since their inception, information technology systems have aided in automating corporate operations, increasing productivity, and maximizing efficiency. Now, businesses can take their perfected processes, standardize them, and sell them to other parties. In today's corporate environment, innovation is critical for survival.
Direct selling:
Direct selling refers to a situation in which a company's goods are immediately accessible from the manufacturer or service provider rather than via intermediate channels. The business avoids the retail margin and any extra expenses connected with the intermediaries in this manner. These savings may be passed on to the client, establishing a consistent sales experience. Furthermore, such intimate touch may help to strengthen client connections. Finally, direct selling benefits consumers by providing convenience and service, such as personal demonstrations and explanations of goods, home delivery, and substantial satisfaction guarantees.
Localized low cost:
In general, this business model is appropriate for standardized goods and services with minimal requirements and low consumer expectations that may be manufactured locally and branded worldwide. However, this company concept will succeed only if the following two criteria are satisfied. The first is contingent upon a sizable market presence in mature markets' urban regions. This circumstance enables businesses to capitalize on their established brand value in developing areas. The second criterion is that the product or service generates revenue or is self-sustaining. This circumstance creates the possibility of reduced earnings in developing economies.
Low-budget innovation:
Fast-moving consumer goods businesses produce co-created items with early adopters through sample testing based on user observation and involvement. As a result, fast-moving consumer goods businesses may obtain a greater new product success rate while incurring fewer development expenses via a low-budget innovation business strategy. That is referred to as low-budget innovation.
Low cost:
A pricing strategy in which a business provides a low price in order to drive demand and increase market share. Additionally referred to as a low-price approach. The low-cost model has sparked a revolution in the airline industry. The end-user benefits from low-cost tickets as a result of a revenue strategy that seeks various sources of income. Ryanair was one of the first businesses to embrace this approach.
Spectrum retail:
Utilizes a multi-tiered e-commerce approach. The firm first focused on business-to-consumer connections with its customers and business-to-business ties with its suppliers. Still, it later expanded to include customer-to-business transactions after recognizing the importance of customer evaluations in product descriptions. It now also enables customer-to-customer transactions by establishing a marketplace that serves as a middleman for such transactions. The company's platform enables nearly anybody to sell almost anything.
Mobile first behavior:
It is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices. The term is “mobile first,” and it is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices.
Long tail:
The long tail is a strategy that allows businesses to realize significant profit out of selling low volumes of hard-to-find items to many customers instead of only selling large volumes of a reduced number of popular items. The term was coined in 2004 by Chris Anderson, who argued that products in low demand or with low sales volume can collectively make up market share that rivals or exceeds the relatively few current bestsellers and blockbusters but only if the store or distribution channel is large enough.
No frills:
A no frills service or product has been stripped of non-essential elements to keep the price low. Initially, the word frills referred to a kind of cloth embellishment. Something provided free of charge to clients may be a frill - for example, complimentary beverages on airline flights or a radio fitted in a rental vehicle. No-frills companies rely on the premise that by eliminating opulent extras, consumers may benefit from reduced costs. Budget airlines, supermarkets, holidays, and pre-owned cars are examples of everyday goods and services with no-frills branding.
Hypermarket:
Disrupts by 'brand bombing' competitors, often by offering below cost. Hypermarkets, like other large-scale retailers, generally operate on a high-volume, low-margin basis. They typically span a space of 5,000 to 15,000 square meters (54,000 to 161,000 square feet) and stock more than 200,000 different brands of goods.
Self-service:
A retail business model in which consumers self-serve the goods they want to buy. Self-service business concepts include self-service food buffets, self-service petrol stations, and self-service markets. Self-service is available through phone, online, and email to automate customer support interactions. Self-service Software and self-service applications (for example, online banking apps, shopping portals, and self-service check-in at airports) are becoming more prevalent.
Two-sided market:
Two-sided marketplaces, also called two-sided networks, are commercial platforms featuring two different user groups that mutually profit from the web. A multi-sided platform is an organization that generates value mainly via the facilitation of direct contacts between two (or more) distinct kinds of connected consumers (MSP). A two-sided market enables interactions between many interdependent consumer groups. The platform's value grows as more groups or individual members of each group use it. For example, eBay is a marketplace that links buyers and sellers. Google connects advertising and searchers. Social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook are also bidirectional, linking consumers and marketers.
Reseller:
Resellers are businesses or individuals (merchants) that acquire products or services to resell them instead of consuming or utilizing them. This is often done for financial gain (but could be resold at a loss). Resellers are well-known for doing business on the internet through websites. One instance is the telecommunications sector, in which corporations purchase surplus transmission capacity or take the call from other providers and resell it to regional carriers.
Technology trends:
New technologies that are now being created or produced in the next five to ten years will significantly change the economic and social landscape. These include but are not limited to information technology, wireless data transmission, human-machine connection, on-demand printing, biotechnology, and sophisticated robotics.
User design:
A client is both the manufacturer and the consumer in user manufacturing. For instance, an online platform could offer the client the tools required to create and market the product, such as product design software, manufacturing services, or an online store to sell the goods. In addition, numerous software solutions enable users to create and customize their products to respond to changing consumer requirements seamlessly.
Online marketplace:
An online marketplace (or online e-commerce marketplace) is a kind of e-commerce website in which product or service information is supplied by various third parties or, in some instances, the brand itself, while the marketplace operator handles transactions. Additionally, this pattern encompasses peer-to-peer (P2P) e-commerce between businesses or people. By and large, since marketplaces aggregate goods from a diverse range of suppliers, the variety and availability are typically greater than in vendor-specific online retail shops. Additionally, pricing might be more competitive.
Sponsorship:
In most instances, support is not intended to be philanthropic; instead, it is a mutually beneficial commercial relationship. In the highly competitive sponsorship climate of sport, a business aligning its brand with a mark seeks a variety of economic, public relations, and product placement benefits. Sponsors also seek to establish public trust, acceptability, or alignment with the perceived image a sport has built or acquired by leveraging their connection with an athlete, team, league, or the sport itself.
Subscription:
Subscription business models are built on the concept of providing a product or service in exchange for recurring subscription income on a monthly or annual basis. As a result, they place a higher premium on client retention than on customer acquisition. Subscription business models, in essence, concentrate on revenue generation in such a manner that a single client makes repeated payments for extended access to a product or service. Cable television, internet providers, software suppliers, websites (e.g., blogs), business solutions providers, and financial services companies utilize this approach, as do conventional newspapers, periodicals, and academic publications.
Target the poor:
The product or service provided here is aimed towards the bottom of the pyramid rather than the top. The target of the flawed business model is a financially feasible strategy that helps low-income communities by integrating them in the value chain of a firm on the demand side as customers and consumers and the supply side as producers, entrepreneurs, or workers in a sustainable manner. While the business earns a little profit on each product sold, it profits from the increased sales volume often associated with a large client base.
Niche retail:
A marketing strategy for a product or service includes characteristics that appeal to a particular minority market segment. A typical niche product will be distinguishable from other goods and manufactured and sold for specialized purposes within its associated niche market. Niche retail has focused on direct-to-consumer and direct-to-business internet sales channels. The slogan for niche retail is Everything except the brand.
Pay as you go:
Pay as you go (PAYG) business models charge based on actual consumption or use of a product or service. Specific mobile phone contracts work on this principle, in which the user may purchase a phone card that provides credit. However, each call is billed separately, and the credit balance is depleted as the minutes are used (in contrast to subscription models where you pay a monthly fee for calls). Pay as you go is another term for pay & go, pay per use, pay per use, or pay-as-you-go.
Supermarket:
A supermarket is a self-service store arranged into aisles and has many foods and home goods. It is bigger and has a greater variety than traditional grocery shops but is smaller and offers a more limited selection than a hypermarket or big-box market. Supermarkets are usually chain shops supplied by their parent firms' distribution centers, allowing for more significant economies of scale. In addition, supermarkets often provide items at competitive rates by using their purchasing power to negotiate lower pricing from producers than smaller shops can.
White label:
The term white label refers to a product or service bought by a reseller who rebrands it to show that the new owner developed it. Frequently, white-label goods are mass manufactured. Thus, white-label goods are produced by one firm and sold by another under their brand and model number. For instance, most Dell computer screens are created by third-party manufacturers yet have the Dell brand and model number.
Mass customization:
Mass customization is a strategy that entails using modular goods and manufacturing processes to allow efficient product individualization. Mass customization refers to producing customized output using flexible computer-aided manufacturing systems in marketing, manufacturing, contact centers, and management. Mass customization is the next frontier for manufacturing and service sectors alike. Beyond the physical product, mass customization is utilized by a diverse variety of software products and services with the goal of developing strong connections with customers via personalization and suggestion.
Remainder retail:
Remainder retail (affectionately referred to as daily deal, flash sale, or one deal a day) is an online business strategy in which a website sells a single product for a period of 24 to 36 hours. Customers may join deal-a-day websites as members and get online deals and invite through email or social media. The deal-of-the-day business model works by enabling merchants to advertise discounted services or goods directly to the deal company's consumers, with the deal company receiving a cut of the retailer's earnings. This enables merchants to foster brand loyalty and rapidly liquidate excess inventory.
Recommended companies based on your search: