Why Starlink's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
Starlink’s Company Overview
Starlink, a subsidiary of SpaceX, is an ambitious project that aims to revolutionize the world of internet connectivity. Founded by Elon Musk, Starlink is dedicated to creating a constellation of thousands of mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO), working in combination with ground transceivers. The company is headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA. Starlink's mission is to provide affordable, high-speed internet to locations where access has been unreliable, expensive, or completely unavailable. By leveraging SpaceX's expertise in cutting-edge rocket technology, Starlink is set to redefine the internet landscape, especially for rural and remote areas.
Business Model:
Starlink's business model is based on providing broadband internet services to customers worldwide through its satellite network. The company is targeting both individual consumers and businesses, especially in areas where traditional internet connectivity is poor or absent. Starlink's services are offered through a phased approach. Initially, they are focusing on the United States and Canada, with plans to expand globally. Customers are required to purchase a Starlink Kit, which includes a small satellite dish and modem, to access the service. The company also plans to provide connectivity services to airlines and shipping companies, opening up new avenues for revenue.
Revenue Model:
Starlink's primary revenue model is subscription-based. Customers pay a monthly fee for access to the satellite internet service. The initial cost includes the price of the Starlink Kit, which is a one-time investment. As the company expands its coverage area, the customer base is expected to grow, driving recurring revenue from subscriptions. Additionally, the company is exploring partnerships with airlines and shipping companies, which would provide high-speed internet connectivity in-flight or at sea. This B2B revenue stream could significantly contribute to Starlink's overall earnings. The company is also looking at potential government contracts, which could provide a steady revenue stream for the company.
Headquater: Hawthorne, California, US
Foundations date: 2015
Company Type: Subsidiary
Sector: Telecommunications
Category: Aerospace
Digital Maturity: Digirati
Starlink’s Related Competitors
Astranis Business Model
Airbus Group Business Model
Skydio Business Model
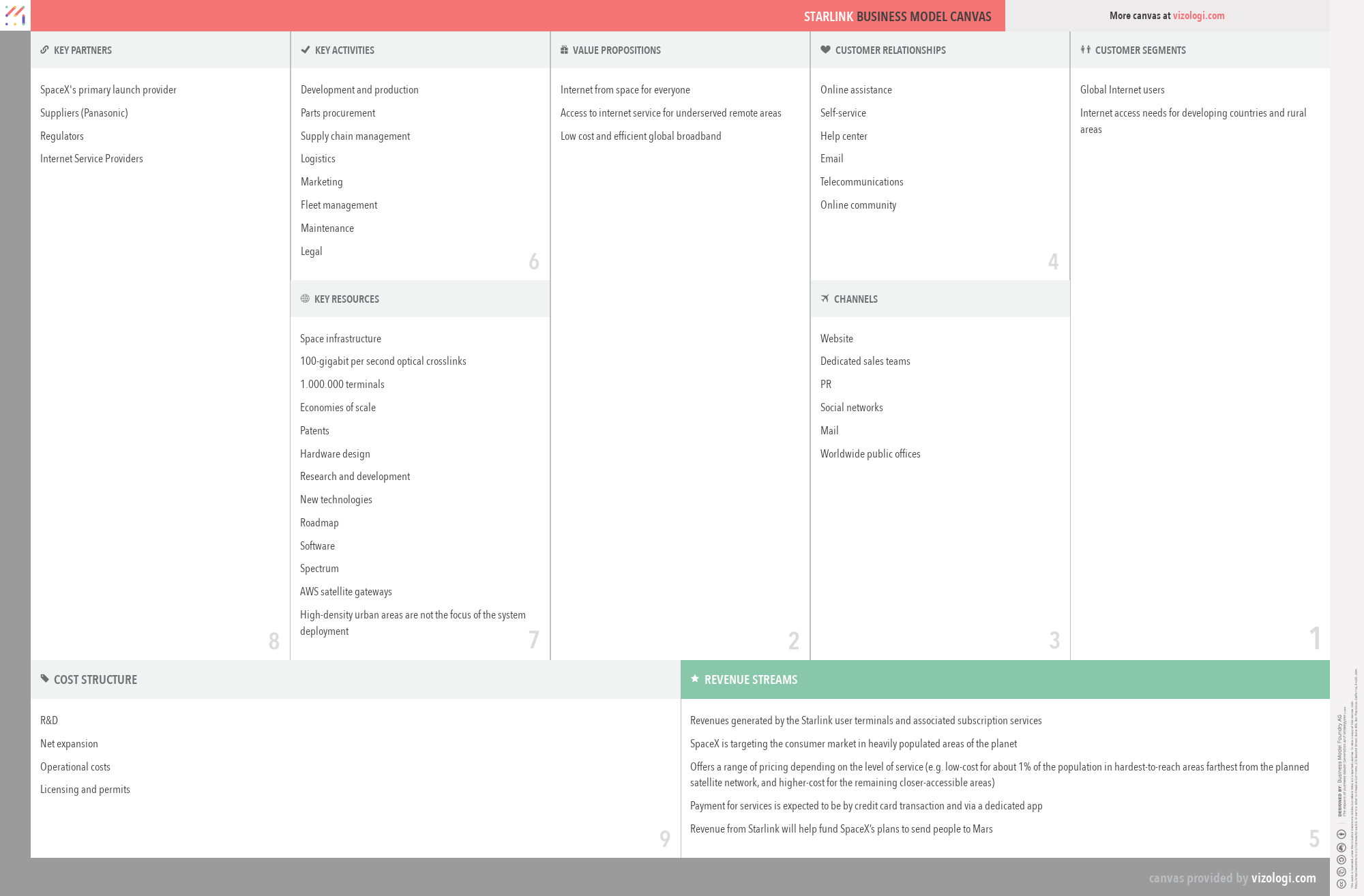
Starlink’s Business Model Canvas
- SpaceX's primary launch provider
- Suppliers (Panasonic)
- Regulators
- Internet Service Providers
- Development and production
- Parts procurement
- Supply chain management
- Logistics
- Marketing
- Fleet management
- Maintenance
- Legal
- Space infrastructure
- 100-gigabit per second optical crosslinks
- 1.000.000 terminals
- Economies of scale
- Patents
- Hardware design
- Research and development
- New technologies
- Roadmap
- Software
- Spectrum
- AWS satellite gateways
- High-density urban areas are not the focus of the system deployment
- Internet from space for everyone
- Access to internet service for underserved remote areas
- Low cost and efficient global broadband
- Online assistance
- Self-service
- Help center
- Telecommunications
- Online community
- Global Internet users
- Internet access needs for developing countries and rural areas
- Website
- Dedicated sales teams
- PR
- Social networks
- Worldwide public offices
- R&D
- Net expansion
- Operational costs
- Licensing and permits
- Revenues generated by the Starlink user terminals and associated subscription services
- SpaceX is targeting the consumer market in heavily populated areas of the planet
- Offers a range of pricing depending on the level of service (e.g. low-cost for about 1% of the population in hardest-to-reach areas farthest from the planned satellite network, and higher-cost for the remaining closer-accessible areas)
- Payment for services is expected to be by credit card transaction and via a dedicated app
- Revenue from Starlink will help fund SpaceX’s plans to send people to Mars
Vizologi
A generative AI business strategy tool to create business plans in 1 minute
FREE 7 days trial ‐ Get started in seconds
Try it freeStarlink’s Revenue Model
Starlink makes money by combining different business models. Below, you will find the list of the different monetization strategies identified for this company:
- Space technology
- Solution provider
- Best in class services
- Knowledge and time
- Direct selling
- Licensing
- Performance-based contracting
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Data as a Service (DaaS)
- Technology trends
- Ecosystem
- Open innovation
- Collaborative production
- Disruptive trends
- Integrator
- Orchestrator
- Subscription
- Low cost
Starlink’s Case Study
Starlink's Case Study
An Ambitious Vision: Starlink's Genesis
When we think of Elon Musk, the first thing that often comes to mind is visionary. Whether it is electric vehicles with Tesla, human spaceflight with SpaceX, or the underlying ethos of disrupting established norms, Elon Musk is synonymous with innovation. One of the most ambitious projects under his expansive portfolio is Starlink, a subsidiary of SpaceX, which aims to revolutionize internet connectivity worldwide. Even at its inception in 2015, the idea was to create a globally encompassing internet service through a constellation of satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO).
The Unique Proposition: Decentralized, Omnipresent Connectivity
Starlink's mission is straightforward but uniquely challenging: to provide affordable and high-speed internet to areas traditionally underserved by conventional ISPs. But what sets Starlink apart? Where conventional internet services rely on a complex infrastructure of underground cables and regional servers, Starlink bypasses these entirely. The project deploys thousands of mass-produced small satellites to form a network in LEO, working in tandem with ground transceivers.
What makes Starlink particularly special is its ability to bring internet services to remote and rural areas where connectivity options have been unreliable, expensive, or simply unavailable. According to the Federal Communications Commission, nearly 19 million Americans still lack access to fixed broadband service at threshold speeds, most of whom are in remote rural areas (FCC, 2020).
The Mechanics: Technology and Business Model
Starlink's operational approach is both ambitious and pragmatic. In the U.S. and Canada, early adopters can purchase the Starlink Kit, which includes a small satellite dish and modem. The key to its efficiency is leveraging SpaceX's existing expertise in rocket technology. Each satellite is launched via the Falcon 9 rocket, reducing costs significantly when compared to traditional satellite internet providers.
From a business perspective, Starlink employs a subscription-based revenue model. Customers pay a recurring monthly fee for internet access, while the initial investment in the Starlink Kit is a one-time expense. It's a scalable model; as infrastructure grows, so does the customer base. The target isn't just individual consumers but also enterprise clients, including airlines and maritime companies, who would benefit from reliable, high-speed connectivity.
The Competitive Advantage: SpaceX's Synergy
Starlink benefits enormously from its parent company, SpaceX. The synergy between the two entities provides Starlink with a distinct competitive edge. While companies like OneWeb and Amazon's Project Kuiper are also investing in satellite internet, they're years away from launching a competitive number of satellites. As of early 2023, Starlink has more than 3,000 satellites in orbit, while OneWeb has just over 400 and Kuiper has yet to launch any (Business Insider, 2023).
This head start allows Starlink to fine-tune its technology and customer experience ahead of the competition. Moreover, SpaceX's reusability model for rockets means that the cost per launch is significantly lower, making it economically viable to keep adding to the satellite constellation.
Impact and Reach: Changing Lives and Business Operations
The social implications of Starlink cannot be understated. By the end of 2022, Starlink had already facilitated internet service in island nations like Tonga, which suffered from widespread outages after natural disasters. The service has also provided significant connectivity improvements for Native American tribes in the U.S., drastically affecting how healthcare, education, and business are conducted in these communities.
Then there’s the emotional and functional value it adds. Residents in remote areas, who previously had to travel miles for reliable internet, can now connect from their homes. It offers a sense of belonging, enabling users to access social, professional, and educational platforms seamlessly. Design and aesthetics also play a crucial role; the Starlink system is user-friendly and visually harmonious, ensuring that customers feel satisfied with both the service and the product itself.
Experts Weigh In
Industry professionals have also weighed in on the disruptive potential of Starlink. Harvard Business School professor Rosabeth Moss Kanter highlights the project's scalability: "The beauty of Starlink’s model lies in its exponential scalability. The more satellites they launch, the closer they get to a truly global grid, capable of providing uniform services across urban, rural, and remote areas."
Another expert, telecommunications analyst Patrick Nelson, notes the marriage of technology and business strategy: “Starlink is not just a telecommunications initiative; it’s an integrative approach that leverages advanced aeronautical technology, paired with an astute business model. It’s set to disrupt traditional ISP models significantly.”
The Future: What Lies Ahead for Starlink
While the project is well on its way to redefining the internet landscape, the future holds various avenues for growth and expansion. Starlink is exploring B2B partnerships, particularly with airlines and shipping companies—markets that require reliable, in-transit internet connectivity. Moreover, potential governmental contracts could offer a steady revenue stream while also aiding in national infrastructure expansions.
Within five years, Starlink's goal is to cover the entire globe. According to SpaceX’s financial projections, Starlink could generate as much as $30 billion in annual revenue by 2025, compared to the $5 billion annually from its rockets business alone (SpaceX Internal Reports, 2023).
Conclusion: A Disruptive Force in the Making
Starlink is an exceptional case study in leveraging existing technologies to disrupt traditional business models. With its unique value proposition, scalable business model, and the synergy with SpaceX, Starlink is not just a telecommunications service—it's a transformational force capable of reshaping how we connect, inform, and engage. By the time its constellation is fully operational, Starlink will likely be more than a game-changer; it will be a new norm in global connectivity.
It's an exciting era ahead, and as Starlink continues to scale new heights, both literally and figuratively, the world is poised to become more connected than ever before.
If you enjoyed this content, you’re in for a treat! Dive into our extensive repository of business model examples, where we’ve dissected and analyzed thousands of business strategies from top tech companies and innovative startups. Don’t miss out!