Why FedEx's Business Model is so successful?
Get all the answers 
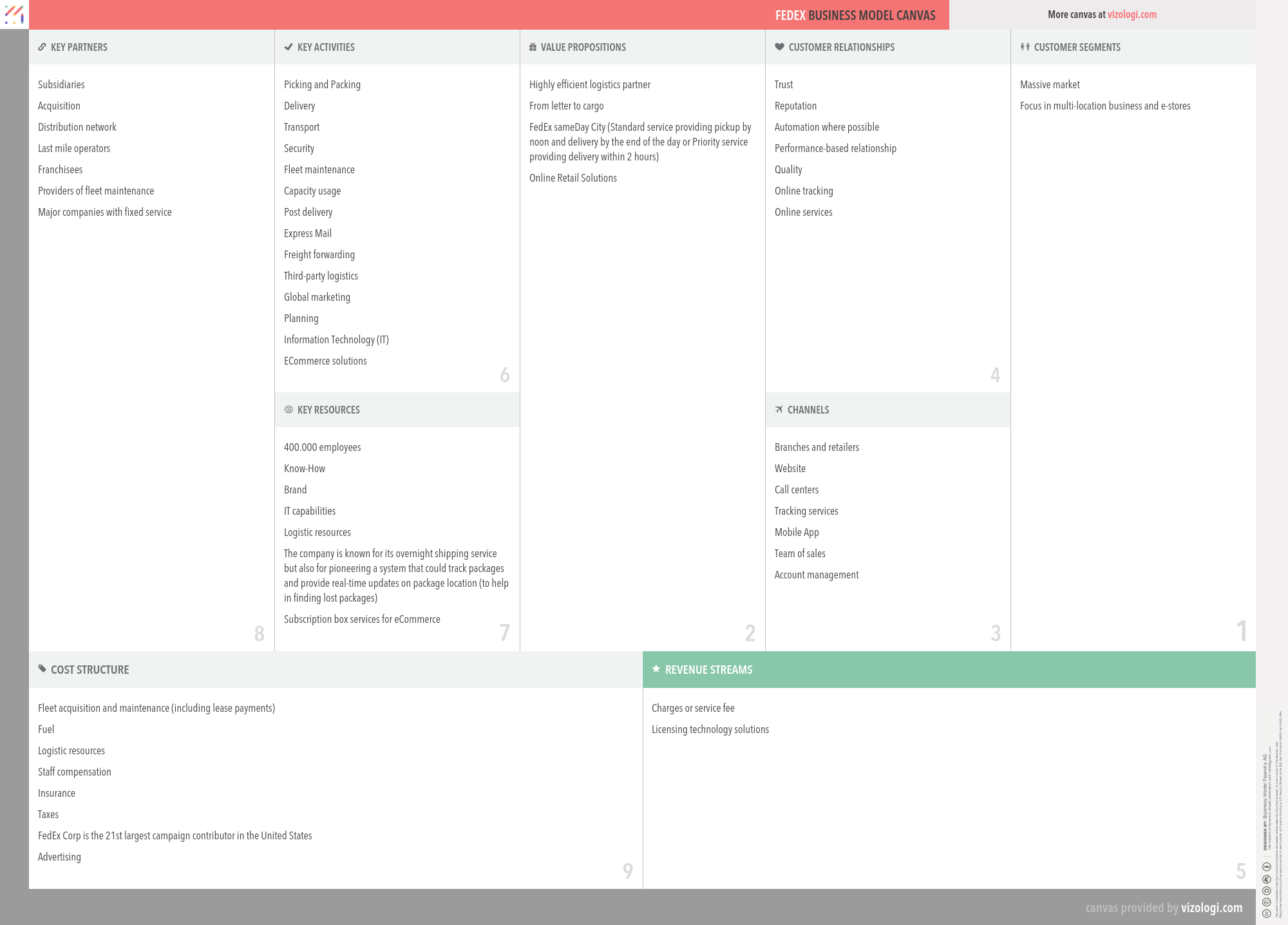
FedEx’s Company Overview
FedEx Corporation (FedEx), incorporated on October 2, 1997, provides a portfolio of transportation, e-commerce and business services through companies competing collectively, operating independently and managed collaboratively, under the FedEx brand. The company's Segments include FedEx Express, TNT Express, FedEx Ground, FedEx Freight and FedEx Services. The FedEx Express Segment offers a range of the United States domestic and international shipping services for delivery of packages and freight.
www.fedex.comFedEx’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing:
Emotional: provides access, badge value, rewards me
Functional: connects, avoid hassles, reduces risks, saves time, reduces effort, organizes, integrates, simplifies, quality, informs
FedEx’s Related Competitors
FedEx’s Business Operations
Add-on:
An additional item offered to a customer of a primary product or service is referred to as an add-on sale. Depending on the industry, add-on sales may generate substantial income and profits for a firm. For example, when a customer has decided to purchase the core product or service, the salesman at an automotive dealership will usually offer an add-on sale. The pattern is used in the price of new software programs based on access to new features, number of users, and so forth.
Best in class services:
When a firm brings a product to market, it must first create a compelling product and then field a workforce capable of manufacturing it at a competitive price. Neither task is simple to perform effectively; much managerial effort and scholarly study have been dedicated to these issues. Nevertheless, providing a service involves another aspect: managing clients, who are consumers of the service and may also contribute to its creation.
Bundling:
Multiple products or services have been bundled together to enhance the value. Bundling is a marketing technique in which goods or services are bundled to be sold as a single entity. Bundling enables the purchasing of several goods and services from a single vendor. While the goods and services are often linked, they may also consist of different items that appeal to a particular market segment.
Cash machine:
The cash machine business model allows companies to obtain money from sales since consumers pay ahead for the goods they purchase, but the costs required to generate the revenue are not yet paid. This increases companies' liquidity, which they may use to pay off debt or make additional investments. Among several others, the online store Amazon often employs this business model.
Cross-subsidiary:
When products and goods and products and services are integrated, they form a subsidiary side and a money side, maximizing the overall revenue impact. A subsidiary is a firm owned entirely or in part by another business, referred to as the parent company or holding company. A parent company with subsidiaries is a kind of conglomerate, a corporation that consists of several distinct companies; sometimes, the national or worldwide dispersion of the offices necessitates the establishment of subsidiaries.
Customer loyalty:
Customer loyalty is a very successful business strategy. It entails giving consumers value that extends beyond the product or service itself. It is often provided through incentive-based programs such as member discounts, coupons, birthday discounts, and points. Today, most businesses have some kind of incentive-based programs, such as American Airlines, which rewards customers with points for each trip they take with them.
eCommerce:
Electronic commerce, or e-commerce (alternatively spelled eCommerce), is a business model, or a subset of a larger business model, that allows a company or person to do business via an electronic network, usually the internet. As a result, customers gain from increased accessibility and convenience, while the business benefits from integrating sales and distribution with other internal operations. Electronic commerce is prevalent throughout all four main market segments: business to business, business to consumer, consumer to consumer, and consumer to business. Ecommerce may be used to sell almost any goods or service, from books and music to financial services and airline tickets.
Integrator:
A systems integrator is an individual or business specializing in integrating component subsystems into a unified whole and ensuring that those subsystems work correctly together. A process is known as system integration. Gains in efficiency, economies of scope, and less reliance on suppliers result in cost reductions and may improve the stability of value generation.
Licensing:
A formal agreement in which the owner of the copyright, know-how, patent, service mark, trademark, or other intellectual property grants a licensee the right to use, manufacture, and sell copies of the original. These agreements often restrict the licensee's scope or area of operation, define whether the license is exclusive or non-exclusive, and stipulate whether the licensee will pay royalties or another kind of compensation in return. While licensing agreements are often used to commercialize the technology, franchisees also utilize them to encourage the sale of products and services.
Pay as you go:
Pay as you go (PAYG) business models charge based on actual consumption or use of a product or service. Specific mobile phone contracts work on this principle, in which the user may purchase a phone card that provides credit. However, each call is billed separately, and the credit balance is depleted as the minutes are used (in contrast to subscription models where you pay a monthly fee for calls). Pay as you go is another term for pay & go, pay per use, pay per use, or pay-as-you-go.
Performance-based contracting:
Performance-based contracting (PBC), sometimes referred to as performance-based logistics (PBL) or performance-based acquisition, is a method for achieving quantifiable supplier performance. A PBC strategy focuses on developing strategic performance measures and the direct correlation of contract payment to success against these criteria. Availability, dependability, maintainability, supportability, and total cost of ownership are all standard criteria. This is accomplished mainly via incentive-based, long-term contracts with precise and quantifiable operational performance targets set by the client and agreed upon by contractual parties.
Solution provider:
A solution provider consolidates all goods and services in a particular domain into a single point of contact. As a result, the client is supplied with a unique know-how to improve efficiency and performance. As a Solution Provider, a business may avoid revenue loss by broadening the scope of the service it offers, which adds value to the product. Additionally, close client interaction enables a better understanding of the customer's habits and requirements, enhancing goods and services.
Sponsorship:
In most instances, support is not intended to be philanthropic; instead, it is a mutually beneficial commercial relationship. In the highly competitive sponsorship climate of sport, a business aligning its brand with a mark seeks a variety of economic, public relations, and product placement benefits. Sponsors also seek to establish public trust, acceptability, or alignment with the perceived image a sport has built or acquired by leveraging their connection with an athlete, team, league, or the sport itself.
Subscription box:
A subscription box is a regular delivery of retail goods to a client. Thus, subscription boxes are both a marketing tactic and a delivery mechanism for products. Subscription boxes are used by subscription-based e-commerce companies, abbreviated subcom, that operates on a subscription-based revenue model. They cater to a diverse client base and address a range of particular demands and interests. Since the subscription box business is still in its infancy, there is little data available. However, between 400 and 600 distinct types of subscription boxes are available in the United States alone, with more known internationally.
Supply chain:
A supply chain is a network of companies, people, activities, data, and resources that facilitate the movement of goods and services from supplier to consumer. The supply chain processes natural resources, raw materials, and components into a completed product supplied to the ultimate consumer. In addition, used goods may re-enter the distribution network at any point where residual value is recyclable in advanced supply chain systems. Thus, value chains are connected through supply chains.
Technology trends:
New technologies that are now being created or produced in the next five to ten years will significantly change the economic and social landscape. These include but are not limited to information technology, wireless data transmission, human-machine connection, on-demand printing, biotechnology, and sophisticated robotics.
Recommended companies based on your search: